21st century
| Millennium |
|---|
| 3rd millennium |
| Centuries |
| Timelines |
| State leaders |
|
| Decades |
|
| Categories: |
|
Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |

The 21st century is the current century in the Anno Domini or Common Era, in accordance with the Gregorian calendar. It began on 1 January 2001 and will end on 31 December 2100. It is the first century of the 3rd millennium.
The rise of a global economy and Third World consumerism marked the beginning of the century, along with increased private enterprise and deepening concern over terrorism after the September 11 attacks in 2001.[1][2][3] The NATO intervention in Afghanistan and the United States-led coalition intervention in Iraq in the early 2000s, as well as the overthrow of several regimes during the Arab Spring in the early 2010s, led to mixed outcomes in the Arab world, resulting in several civil wars and political instability.[4] The 2020s saw an increase in wars across the world, as seen with conflicts such as the Russian Invasion of Ukraine and the Israel-Hamas war.[5][6] The United States has remained the sole global superpower, while China is now considered to be an emerging superpower.
In 2022, 45% of the world's population lived in "some form of democracy", although only 8% lived in "full democracies".[7] The United Nations estimates that by 2050, two thirds of the world's population will be urbanized.
The world economy expanded at high rates from $42 trillion in 2000 to $101 trillion in 2022, and though many economies rose at greater levels, some gradually contracted.[a] The European Union greatly expanded in the 21st century, adding 13 member states, but the United Kingdom withdrew. Most EU member states introduced a common currency, the Euro. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), also greatly expanded, adding 13 member states.
Effects of global warming and rising sea levels exacerbated the ecological crises, with eight islands disappearing between 2007 and 2014.[8][9][10]
Globally, from January 2020 to May 2023, the COVID-19 pandemic began to rapidly spread worldwide, causing more than 7 million reported deaths,[11] and around 18.2 to 33.5 million estimated deaths,[12] while at the same time, causing severe global economic disruption, including the largest global recession since the Great Depression in the 1930s.[13]
Due to the sudden proliferation of internet-accessible mobile devices, such as smartphones becoming ubiquitous worldwide beginning in the early 2010s, more than two thirds of the world's population obtained access to the Internet by 2023.[14] After the success of the Human Genome Project, DNA sequencing services became available and affordable.[15][16] There were significant improvements in the complexity of artificial intelligence, with American companies, universities, and research labs pioneering advances in the field.[17] Generative AI-based applications such as ChatGPT and DALL-E have accumulated billions of users, and allow users to instantly generate complex texts, images, art, and video, comparable to the sophistication of human work.[18] Research into outer space greatly accelerated in the 2020s, with the United States mainly dominating space exploration, including the James Webb Space Telescope, Ingenuity helicopter, Lunar Gateway, and Artemis program.[19][20]
Pronunciation
There is a lack of general agreement over how to pronounce specific years of the 21st century in English. Academics have pointed out that the early years of previous centuries were commonly pronounced as, for example, "eighteen oh five" (for 1805) and "nineteen oh five" (for 1905).[21] Generally, the early years of the 21st century were pronounced as in "two-thousand (and) five," with a change taking place around 2010, when pronunciations often shifted between the early-years form of "two-thousand and ten" and the traditionally more concise form of "twenty-ten."
The Vancouver Olympics, which took place in 2010, was being officially referred to by Vancouver 2010 as "the twenty-ten Olympics".[further explanation needed]
Society

Technologies such as ultrasound, prenatal genetic testing and genetic engineering have advanced significantly. Because of sex-selective abortion, fewer girls have been born in the 21st century (and since the early 1980s) compared to past centuries, mostly because of son preference in East and South Asia. In 2014, only 47 percent of Indian births were of girls.[22] This has led to an increase in bachelors in countries such as China and India. The first genetically modified children were born November 2018 in China to significant controversy, beginning a new biological era for the human species.[23]
Anxiety[24] and depression[25] rates have risen in the United States and many other parts of the world. However, suicide rates have fallen in Europe and most of the rest of the world so far this century, declining 29% globally between 2000 and 2018, despite rising 18% in the United States in the same period. The decline in suicide has been most notable among Chinese and Indian women, the elderly, and middle-aged Russian men.[26][27]
Knowledge and information
The entire written works of humanity, from the beginning of recorded history to 2003, in all known languages, are estimated to amount to five exabytes of data.[28][29] Since 2003, with the beginning of social media and "user-generated content", the same amount of data is created every two days.[30] With the AI boom of the 2020s gaining international prominence, as of 2024, mass-produced AI-generated content comprised over half of the Internet.[31]
Telecommunications in the early 21st century are much more advanced and universal than they were in the late 20th century. Only a few percent of the world's population were Internet users and cellular phone owners in the late 1990s; while as of 2023, 67% of the world's population is online,[14] and 78% of all people aged 10 and above own a mobile phone.[32] In the 2010s, artificial intelligence, mainly in the form of deep learning and machine learning, became more prevalent and in the early 2020s, with the rise of generative AI, the AI boom began. As of 2022, 8.6% of the world's population still lacked access to electricity.[33]

In 2001, Dennis Tito became the first space tourist, beginning the era of commercial spaceflight. Entrepreneurs Elon Musk and Richard Branson are working towards commercial space exploration, colonization and tourism, while China and India have made substantial strides in their space programs. On 3 January 2019, China landed a robotic spacecraft on the far side of the Moon, the first to do so.[34] On 23 August 2023, with the Chandrayaan-3 Mission, India became the first country to touch down near the lunar south pole.[35]
Culture and politics
War and violence have declined considerably compared to the 20th century, continuing the post-World War II trend called Long Peace. However, since the beginning of the 2020s, geopolitical tensions and wars have been rising across the world, as seen with the deterioration of US-China relations,[36] Russian Invasion of Ukraine, Tigray War, Sudanese civil war, Israel–Hamas War, etc.[5][6]
Poverty is still widespread globally, but fewer people live in the most extreme forms of poverty. In 1990, 37.9% of the world's population lived in extreme poverty; by 2022, this had dropped to just 9%.[37]
The Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data scandal drew international attention to the possible adverse effects of social media in influencing citizen's views, particularly regarding the 2016 United States presidential election.[further explanation needed]
Population and urbanization
The world population was about 6.1 billion at the start of the 21st century and reached 8 billion by November 2022. It is estimated to reach nearly 8.6 billion by 2030,[38] and 9.8 billion by 2050. According to the United Nations World Urbanization prospects, 60% of the world's human population are projected to live in megacities and megalopolises by 2030, 70% by 2050, and 90% by 2080.[39]
Life expectancy has increased as child mortality continues to decline. A baby born in 2019, for example, will, on average (globally), live to 73 years—27 years longer than the global average of someone born in 1950.[40] Ten million Britons (16% of the United Kingdom population) will, on average, live to 100 or older.[41]
Climate change remains a serious concern; UN Chief António Guterres, for instance, has described it as an "existential threat" to humanity.[42] Furthermore, the Holocene extinction event, the sixth most significant extinction event in the Earth's history, continues with the widespread degradation of highly biodiverse habitats as a by-product of human activity.[43]

Economics, education and retirement
Economically and politically, the United States and Western Europe were dominant at the beginning of the century; by the 2010s, China became an emerging global superpower and, by some measures, the world's largest economy. In terms of purchasing power parity, India's economy became more significant than Japan's around 2011.[44]
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are decentralized currencies that are not controlled by any central bank. These currencies are increasing in popularity worldwide due to the expanding availability of the internet and are mainly used as a store of value.
There is an ongoing impact of technological unemployment due to automation and computerization: the rate at which jobs are disappearing—due to machines replacing them—is expected to escalate.[45] Automation alters the number of jobs and the skills demands of industries. As of 2019, the production output of first world nations' manufacturing sectors was doubled when compared to 1984 output; but it is now produced with one-third fewer workers and at significantly reduced operating costs.[46] Half of all jobs with requirements lower than a bachelor's degree are currently in the process of being replaced with partial- or full-automation.[47]
The World Economic Forum forecast that 65% of children entering primary school will end up in jobs or careers that currently do not yet exist.[48]
A rise in the retirement age has been called for in view of an increase in life expectancy and has been put in place in many jurisdictions.[49][50]
Linguistic diversity
As of 2009, Ethnologue catalogued 6,909 living human languages.[51] The exact number of known living languages will vary from 5,000 to 10,000, generally depending on the precision of one's definition of "language", and in particular, on how one classifies dialects.
Estimates vary depending on many factors, but the general consensus is that there are between 6,000 and 7,000 languages currently spoken. Between 50% and 90% of those will have become extinct by the year 2100.[52]
The top 20 languages spoken by more than 50 million speakers each, are spoken by 50% of the world's population. In contrast, many of the other languages are spoken by small communities, most of them with fewer than 10,000 speakers.[52]
Events
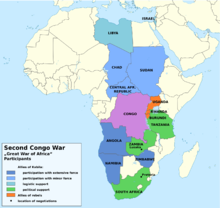




- 1998–2003 – The Second Congo War continued into the early 21st century. A 1999 ceasefire quickly broke down and a UN peacekeeping mission, MONUC, was unable to control the fighting. Troops from Rwanda and Uganda continued to support rebel groups against the Democratic Republic of the Congo and rifts also grew between Rwanda and Uganda as they accused each other of supporting rival rebel groups as well. Laurent Kabila, president of the DRC, was assassinated in January 2001 and his son, Joseph Kabila, took power. Throughout 2002 steps were made towards peace and Rwanda and Uganda both removed their troops from the country. On December 17, 2002, a massive treaty officially ended the war. However, the DRC only holds power in less than half of the country, with most of the eastern and northern portions still controlled by rebel groups, where there is still significant infighting. In addition, Rwanda still supports anti-DRC rebels and anti-Rwandan rebels continue to operate from the DRC. The war killed an estimated 3.9 million people, displaced nearly 5.5 million, and led to a widespread and ongoing famine that continues to result in deaths. Severe human rights violations continue to be reported.[53]
- 2000–2005 – The Second Intifada, a major Palestinian uprising against Israel, is estimated to have led to the deaths of approximately 3,000 Palestinians and 1,000 Israelis.[citation needed]
2001
- January 20:
- George W. Bush is inaugurated as the 43rd president of the United States. He is the second president from the Bush family, after his father.
- President Joseph Estrada of the Philippines is ousted in the Second EDSA Revolution.
- January 26 – An earthquake strikes Gujarat, India, on Republic Day, resulting in more than 20,000 deaths.
- April 1 – The Netherlands becomes the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage.
- May 13 – Conservative media magnate Silvio Berlusconi wins the general election in Italy, becoming the country's Prime Minister. Berlusconi would go on to dominate Italian politics for the rest of the decade.
- June 1 – The Nepalese royal massacre occurs at a house on the grounds of the Narayanhity Royal Palace, the residence of the Nepalese monarchy. Ten members of the family were killed during a party or monthly reunion dinner of the royal family in the house. The dead included King Birendra of Nepal and Queen Aishwarya.
- July 20 – 22 – More than 200,000 anti-globalization protesters march in Genoa, during the 27th G8 summit. Two demonstrators are killed by the Italian police. On July 21, a group of Carabinieri attacked the school Armando Diaz, critically injuring many peaceful protesters.
- September 11 – September 11 attacks – Nineteen al-Qaeda terrorists hijack four commercial airliners and crash two of them into the World Trade Center, one into the Pentagon and one into a field in Shanksville, Pennsylvania, of the United States on 11 September, killing nearly 3,000 people. The president George W. Bush subsequently declares the War on Terror.
- October 23 – Steve Jobs introduces the first iPod.
- December 11 – After 15 years of negotiations, the People's Republic of China becomes a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- 2001–2014 – The Northern Alliance and NATO-led ISAF invades Afghanistan on October 7, 2001, and overthrows the Al-Qaeda-supportive Taliban government. Troops remained to install a democratic government, fight a slowly escalating insurgency, and to hunt for Al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden who would be killed by American troops nearly 10 years later, on May 2, 2011. On December 24, 2014, NATO forces officially ended combat operations in Afghanistan, but forces remained until August 30, 2021, followed by a quick withdrawal of all troops.
2002
- January 1:
- The Open Skies mutual surveillance treaty, initially signed in 1992, officially enters into force.[54]
- The Euro is the official currency introduced in the Eurozone countries.[55] The former currencies of all the countries that use the Euro ceased to be legal tender on February 28.[56]
- January 6 – The Boston Globe publishes results of an investigation leading to the criminal prosecutions of five Roman Catholic priests and bringing widespread attention to the sexual abuse of minors by Catholic clergy.[57]
- January 17 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, displacing an estimated 400,000 people.[58]
- January 18 – The Sierra Leone Civil War comes to a conclusion with the defeat of the Revolutionary United Front by government forces.[59]
- February 6 – Queen Elizabeth II of the Commonwealth realms celebrates her Golden Jubilee, marking 50 years since her accession to the thrones of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand.[60]
- February 8 – 24 – The 2002 Winter Olympics are held in Salt Lake City, Utah.[61]
- February 12 – The trial of Slobodan Milošević, the former president of Yugoslavia, begins at the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia in The Hague.[62]
- February 14 – The State of Bahrain is declared a constitutional monarchy and becomes the Kingdom of Bahrain.[63]
- February 19 – NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey space probe begins to map the surface of Mars using its thermal emission imaging system.[64]
- February 20 – 2002 El Ayyat railway accident: A train fire in El Ayyat, Egypt kills at least 370 people.[65]
- February 22:
- UNITA guerrilla leader Jonas Savimbi is killed in clashes against government troops led by Angolan President José Eduardo dos Santos in Moxico Province, Angola.[66]
- The government of Sri Lanka and the Tamil Tigers agree to a ceasefire, temporarily ending the Sri Lankan Civil War.[67] It would last until the resumption of hostilities in 2008.[68]
- February 27 – A mob attacks a train near Godhra, India, killing approximately 59 people.[69] The state of Gujarat breaks out into riots, including the Gulbarg Society massacre on February 28 that kills approximately 69 people.[70]
- March 14 – SpaceX is founded by Elon Musk.
- May 20 – After a long period of occupation by Indonesia, East Timor's independence is recognized by Portugal and the UN.
- July 1 – The International Criminal Court (ICC) is established.
- September 10 – Switzerland, a neutral country, becomes a member of the United Nations.
- October 12 – Jemaah Islamiyah, a violent Islamist group, claims responsibility for the detonation of three bombs in the tourist district of Kuta on the Indonesian island of Bali. The attack killed 202 people and left 209 people injured.
- November 15 – Hu Jintao becomes the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party, making him the paramount leader of China after Jiang Zemin.
2003
- January 10 – North Korea announces its withdrawal from the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons.
- February 4 – The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia is renamed to "Serbia and Montenegro" (after its two constituent states) after its leaders reconstitute the country into a loose state-union between Montenegro and Serbia, ending the 73-year-long use of the name "Yugoslavia" by a sovereign state.
- 2003–2020 – In February 26, 2003, a conflict in Darfur, Sudan begins and escalates into full-scale war. By 2008 it was believed that up to 400,000 people had been killed and over 2.5 million displaced. In 2005, the ICC decided that Darfur war criminals would be tried, and on July 14, 2008, Sudanese president Omar al-Bashir was charged with 5 accounts of crimes against humanity and 2 accounts of war crimes, even though the ICC had no power to enforce such charges. The war ends following a peace agreement on August 31, 2020.
- 2003–2010 – The U.S.-led coalition invades Iraq on March 20, 2003, and overthrows the government of Saddam Hussein (who is executed by the Iraqi government on December 30, 2006). Coalition troops remain in the country to install a democratic government and fight an escalating insurgency. In addition to an insurgency against the American presence, Iraq also suffered from a civil war for several years. The war was soon seen as the central front of the War on Terror by many governments, despite growing international dissatisfaction with the war. The total death toll has been estimated at near 150,000 but these estimations are highly disputed, with one highly disputed study guessing even over 1 million.[71] After the U.S.-led coalition initiated a troop surge in 2007, casualty numbers have decreased significantly. Combat ended, at least officially, in August 2010.
- April 14 – The Human Genome Project is completed, with 99% of the human genome sequenced to 99.99% accuracy.
- August 27 – Mars makes its closest approach to Earth in over 60,000 years.
- November 3 – 23 –The Rose Revolution occurs in Georgia.
- November 17 – Arnold Schwarzenegger becomes Governor of California.
- December 19 – Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi announces that Libya would voluntarily eliminate all weapons of mass destruction.
2004
- February 4 – TheFacebook, later renamed to Facebook, is formed by Mark Zuckerberg, Andrew McCollum, Eduardo Saverin, Dustin Moskovitz, and Chris Hughes.
- March 11 – Ten explosions occur at the Cercanías commuter train system of Madrid, Spain, killing 191 people and injuring around 2,000.
- May 1 – The European Union expands by 10 countries (including eight former communist countries, plus Malta and Cyprus).
- June 5 – Former U.S. president Ronald Reagan dies at the age of 93, after suffering nearly a decade from Alzheimer's disease.
- September 1 – A group of Chechen rebels invade a school in Beslan, keeping thousands of hostages during three days. A series of shootings and bombings kills 334 people and injured 750.
- 2004–2005 – Beginning on November 22, 2004 and ending on January 23, 2005, the Orange Revolution occurs in Ukraine.
- November 11 – Palestinian leader and Chairman of the Palestine Liberation Organization Yasser Arafat dies in France, at the age of 75, from hemorrhagic stroke.
- November 18 – Massachusetts becomes the first U.S. state to legalize same-sex marriage.
- December 26 – 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami leaves 227,898 dead.
2005
- January 1 – Jeanna Giese becomes the first person to ever survive rabies without a vaccination.[72][73]
- January 5 – Eris, the most massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System, is discovered by a team led by Michael E. Brown using images originally taken on October 21, 2003, at the Palomar Observatory.[74]
- January 12 – Deep Impact is launched from Cape Canaveral with the purpose of studying the comet Tempel 1.[75]
- January 14 – The Huygens spacecraft lands on Titan, the largest moon of Saturn.[76]
- January 20 – The most intense solar particle event in recorded history is observed.[77]
- February 14 – YouTube is founded by Jawed Karim, Chad Hurley and Steve Chen.
- February 14 – April 27 – Cedar Revolution occurs in Lebanon.
- February 16 – The Kyoto Protocol comes into effect.
- March 22 – April 11 – Tulip Revolution occurs in Kyrgyzstan.
- April 19 – After the death of Pope John Paul II on April 2, Joseph Ratzinger of Germany is elected as Pope Benedict XVI.
- July 7 – Four Islamic extremist suicide bombers set off three bombs in London; 56 people are killed, including the four suicide bombers.
- November 22 – Angela Merkel becomes the first elected female Chancellor of Germany.
2006
- January 16 – Ellen Johnson Sirleaf becomes President of Liberia, and thus Africa's first elected female head of state.
- March 21 – Twitter is founded by Jack Dorsey, Noah Glass, Biz Stone, and Evan Williams.
- April 23 – Spotify is founded by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon.
- May 21 – June 3 – The State Union of Serbia and Montenegro is peacefully dissolved and Serbia and Montenegro emerge as independent and sovereign nations.
- July 12 – Hezbollah crosses the border of Lebanon and captures two Israeli soldiers. Israel responds by sending troops across the border and bombing Hezbollah strongholds, while Hezbollah fires missiles on towns in northern Israel, approximately 6 each day. At the end of the war 1,200 Lebanese civilians, 500 Hezbollah fighters, 44 Israeli civilians and 121 Israeli soldiers die. A ceasefire is signed on August 14, after which Israeli troops withdrew from Lebanon.
- October 9 – North Korea conducts its first nuclear test.[78] This was preceded by years of political wrangling with the U.S. over the status of their nuclear program.
2007
- January 1 – Bulgaria and Romania join the European Union.
- January 9 – Apple CEO Steve Jobs introduces the original iPhone at a Macworld keynote in San Francisco, starting the new era of smartphones with this invention.
- January 25 – A civil war escalates in the Gaza Strip throughout June, which would result in the Hamas driving most Fatah-loyal forces out from the Strip. In reaction, Palestinian president Mahmoud Abbas dismisses Hamas Prime Minister Ismail Haniyeh and dissolves the Hamas-ruled parliament. Scattered conflict continues.
- January 31 – Boston faces a hoax bomb scare, as a result of LED placards of Ignignokt and Err from Aqua Teen Hunger Force being mistaken as an improvised explosive device[79]
- July 25 – Pratibha Patil becomes the first woman to be elected President of India.
- December 13 – 27 EU member states sign the Treaty of Lisbon, with the treaty coming into effect on December 1, 2009.
- 2007–2008 – Crisis follows the Kenyan presidential election of 2007, leading to the formation of a coalition government, with Mwai Kibaki as president and Raila Odinga as prime minister.
2008
- January 1 – Cyprus and Malta adopt the euro currency.[80][81]
- January 14 – At 19:04:39 UTC, the uncrewed MESSENGER space probe is at its closest approach during its first flyby of the planet Mercury.[82]
- January 21:
- Stock markets around the world plunge amid growing fears of a U.S. Great Recession, fueled by the 2007 subprime mortgage crisis.[83]
- Online activist group Anonymous initiates Project Chanology, after a leaked interview of Tom Cruise by the Church of Scientology is published on YouTube, and the Church of Scientology issued a "copyright infringement" claim. In response, Anonymous sympathizers took to the streets to protest outside the church (after February 10), while the church's websites and centres were getting DoS attacks, phone line nukes, and black faxes.[84][85][86][87]
- February 16 – Kosovo unilaterally declares independence from Serbia. Serbia refuses to recognize it and considers Kosovo as part of its territory.
- February 18 – WikiLeaks releases allegations of illegal activities carried out by the Cayman Islands branch of Swiss banking corporation Julius Baer; a subsequent lawsuit against WikiLeaks prompts a temporary suspension of the website, but uproar about violations of freedom of speech causes WikiLeaks to be brought back online.[88][89]
- May 2 – Cyclone Nargis kills 133,000 in Myanmar.
- May 12 – Magnitude 8.0 earthquake occurs in Wenchuan, China, causing almost 90,000 people to die or go missing.
- May 28 – The 1st Nepalese Constituent Assembly declares Nepal a republic, ending its monarchy.
- August 1 – 12 – An armed conflict is fought between Georgia and the Russian Federation together with Ossetian and Abkhazian separatists on the other. Russia officially recognizes independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.
- November 4 – Barack Obama is elected as the first African-American president of the United States. He is sworn into office in January 20, 2009.
- November 26 – 29 – The financial capital of India, Mumbai, is attacked by 10 Pakistani terrorists belonging to Lashkar-e-Taiba, resulting in 175 deaths (including 9 attackers). One gunman named Ajmal Amir Kasab was captured alive by Mumbai Police and was executed on 21 November 2012.
- December 11 – Following the release of its beta version on September 2, Google Chrome 1.0 is released.
2009

- January 3 – The cryptocurrency Bitcoin is launched.
- January 15 – US Airways Flight 1549 ditches in the Hudson River in an accident that becomes known as the "Miracle on the Hudson", as all 155 people on board are rescued.
- April 1 – Albania and Croatia join NATO.[90]
- April 5 – North Korea launches a rocket from its Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground, which it says is carrying the Kwangmyŏngsŏng-2 satellite, prompting an emergency meeting of the United Nations Security Council.[91]
- April 7 – April 2009 Moldovan parliamentary election protests – In protests that spurred across Moldova, claiming a fraudulent election had occurred, 4 people died and 270 were injured.
- April 21 – UNESCO launches The World Digital Library.[92]
- June 13 – Protests erupt in Iran, following the presidential election against Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad.
- June 16 – BRIC is formed by Brazil, Russia, India, and China, as an economic bloc.
- June 25 – American pop star Michael Jackson dies at the age of 50. His death triggers an outpouring of worldwide grief; online reactions to the event cripple several major websites and services, as the abundance of people accessing the web addresses pushes internet traffic to unprecedented and historic levels.[93]










2010
- February 25 – Kamla Persad-Bissessar becomes the first female Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago.
- April 10 – Polish President Lech Kaczyński dies in an airplane crash near the city of Smolensk, Russia, along with his wife and 94 other people on board.
- June 11 – July 11 – South Africa becomes the first country in Africa to host the FIFA World Cup.
- June 24 – Julia Gillard becomes the first female Prime Minister of Australia.
- October 3 – Dilma Rousseff is elected as the first female president of Brazil. She serves as the president until her impeachment and removal from office on August 31, 2016.
- November 13 – Burmese opposition leader and 1991 Nobel Peace Prize laureate Aung San Suu Kyi is released from house arrest, after being incarcerated since 1989.
- December 17 – The Arab Spring, a revolutionary wave, begins in Tunisia, and eventually spreads across the Middle East and the Arab world, with widespread protests, demonstrations, riots and civil wars for free elections and human rights.
2011
- March 11 – The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and subsequent Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan leave 15,899 dead.
- May 2 – Al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden, the mastermind behind the 9/11 attacks, is killed in a raid at his compound in Abbottabad, Pakistan by the U.S. Navy's SEAL Team 6 (DEVGRU).
- July 10 – Britain's largest tabloid newspaper, the News of the World, shuts down after 168 years in print due to the 2009 phone hacking scandal.
- July 14 – South Sudan, following the January 2011 independence referendum, becomes a member of the United Nations.
- September 17 – The Occupy movement, an international protest movement against social and economic inequality, takes shape. It is partially inspired by the Arab Spring and is one of the first significant global protest movements to occur in the age of social media.
- October 20 – Deposed dictator Muammar Gaddafi is captured and killed by the National Liberation Army of Libya, during the Libyan Civil War.
- November 16 – Italy's long-term Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi resigns amid public protests, financial crisis and sexual scandals.
- December 15 – The Iraq War is formally declared over.
- December 17 – Kim Jong-il, supreme leader of North Korea, dies. He is succeeded by his son Kim Jong-un.
2012

- November 15 – Xi Jinping becomes the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party, making him the paramount leader of China after Hu Jintao.
- December 10 – Séléka rebels seize power in the Central African Republic, ousting the President and government and beginning a civil war.
- December 19 – Park Geun-hye is elected President of South Korea, the first woman to hold the position.
2013
- January 11 – France intervenes with its army in the Northern Mali conflict, defeating the Islamists who had taken control of the country.
- February 28 – Pope Benedict XVI resigns, becoming the first pope to do so since 1415. Benedict takes the title pope emeritus. At the subsequent papal conclave, Cardinal Jorge Mario Bergoglio of Argentina is elected pope on March 13, becoming the first Latin American pope. Bergoglio takes the name of Pope Francis.
- March 5 – President of Venezuela Hugo Chávez dies due to prostate cancer and is succeeded by Nicolás Maduro.
- March 21 – Convicted Kurdish leader Abdullah Ocalan puts an end to the armed revolt against Turkey.
- April 8 – British politician and former Prime Minister of the UK Margaret Thatcher dies at the age of 87, from a stroke.
- July 1 – Croatia becomes the 28th member of the European Union.
- September 14 – Syria avoids an American intervention on its soil during the Syrian Civil War, accepting to destroy all chemical weapons stocks owned.
- November – China declares an "Air Defense Identification Zone" in the East China Sea, including over the Senkaku Islands, a group of islands held by Japan, but claimed by both Japan and China, and the Socotra Rock, claimed by both China and South Korea.
- December 5 – South African political and civil leader Nelson Mandela dies at the age of 95, from natural causes.
- December 15 – The South Sudanese Civil War breaks out.
- Iran allows international inspections on its nuclear policy in exchange of the removal of the sanctions and the right to produce a small amount of low-grade enriched uranium, thus marking an apparent new policy towards the United Nations under Hassan Rohani's presidency.
- 2013–2014 – A political crisis in Thailand breaks out and the government declares martial law.
2014
- February 22 – Pro-Russian President of Ukraine Viktor Yanukovich is ousted amidst the Euromaidan revolution. The Russian Federation annexes Crimea in response, and a "low intensity" war in Donbas breaks out between the Ukrainian government and Russian-backed separatists.
- May 26 – Narendra Modi becomes 14th Prime Minister of India, winning a clear majority in the election.
- September 18 – Scotland votes to remain part of the United Kingdom during the 2014 Scottish independence referendum.
- September–October – During the Syrian civil war, the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant rises and seizes territories in northern Iraq and Syria, near the border with Turkey. The United States lead a coalition of more than 30 countries to destroy ISIL. Meanwhile, Russia leads its own coalition, along with Syria, Iraq and Iran, and Russia's military action begins on September 30, 2015.
- October 31 – In Burkina Faso, President Blaise Compaoré resigns amidst widespread protests, ending 27 years of leadership.
- December 17 – United States President Barack Obama and Cuban President Raúl Castro announce the beginning of a process of normalizing relations between Cuba and the United States, ending a 54-year stretch of hostility between the two nations. Later, on July 20, 2015, with full diplomatic relations, the embassies of both countries are opened after five decades.
2015
- January 7 – Two gunmen, brothers Saïd and Chérif Kouachi, commit a mass murder at the offices of Charlie Hebdo in Paris, killing 12 people. Following the attack, about two million people, including more than 40 world leaders, met in Paris for a rally of national unity, and 3.7 million people joined demonstrations across the country. The phrase Je suis Charlie became a common slogan of support at the rallies and in social media.
- March 6 – NASA's Dawn probe enters orbit around Ceres, becoming the first spacecraft to visit a dwarf planet.[94][95]
- March 23 – Singaporean politician and the 1st Prime Minister of Singapore Lee Kuan Yew dies at the age of 91.
- April 25 – A magnitude 7.8 earthquake strikes Nepal and causes 8,857 deaths[96][97] in Nepal, 130 in India,[98] 27 in China[99] and 4 in Bangladesh[100] with a total of 9,018 deaths.
- April 29 – The World Health Organization (WHO) declares that rubella has been eradicated from the Americas.[101]
- June 26 – The Supreme Court of the United States determines that same-sex couples have a constitutional right to marry in a landmark case Obergefell v. Hodges.
- July 14 – The P5+1 (China, France, Russia, the UK, and the US + Germany) and Iran agree on final provisions of Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action in regards to the latter's nuclear program.
- October – The Chinese Communist Party announces the end of the one-child policy after 35 years.
- November 13 – ISIL claims responsibility of the November 2015 Paris attacks, which killed 137 and left 416 injured.
- November 24 – Turkey shoots down a Russian Sukhoi Su-24M attack aircraft. This is the first case of a NATO member destroying a Russian aircraft since the attack on the Sui-ho Dam (during the Korean War).
- November 30 – December 12 – During the UN summit on Climate Change, 193 nations agree to reduce carbon emissions starting in 2020.
- During the 2015 European migrant crisis, around 1.3 million people, most notably refugees of the wars in Syria, Iraq and Afghanistan, flee to Europe to claim asylum, leading to considerable political upheaval in the European Union. Germany ultimately takes in the majority of the asylum seekers.
2016
- January 3 – Following the fallout caused by the execution of Nimr al-Nimr, Saudi Arabia and several other countries end their diplomatic relations with Iran.[102]
- January 8 – Joaquín Guzmán, widely regarded as the world's most powerful drug trafficker, is recaptured following his escape from a maximum-security prison in Mexico.[103]
- January 16
- The International Atomic Energy Agency announces that Iran has adequately dismantled its nuclear weapons program, allowing the United Nations to lift sanctions immediately.[104]
- In the general election of the Republic of China (Taiwan), the Democratic Progressive Party, led by Tsai Ing-wen, secured a majority in the Legislative Yuan, resulting in the first majority by a non-KMT party and the first majority won by the DPP. Tsai become the 14th President for Taiwan, and also become the first female leader for China.[105]
- January 28 – The World Health Organization announces an outbreak of the Zika virus.[106]
- June 5 – Hillary Clinton becomes the Democratic Party's nominee for president of the United States, making her the first woman to be nominated for president by a major party.
- June 23 – The United Kingdom votes to leave the European Union in the June 2016 membership referendum.
- July 15 – 16 – A coup d'état is attempted in Turkey against state institutions, including but not limited to the government and President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan. The attempt is carried out by a faction within the Turkish Armed Forces that organized themselves as the Peace at Home Council.
- September 2 – 1st President of Uzbekistan Islam Karimov dies at age of 78, after 25 years in office.
- September 28 – Former President of Israel and 1994 Nobel Peace Prize laureate Shimon Peres dies at the age of 93, from a massive stroke.
- October 13 – Bhumibol Adulyadej, the longest-reigning Thai monarch dies at the age of 88, from a long illness.
- November 8 – Donald Trump is elected as the 45th president of the United States, defeating Hillary Clinton.
- November 25 – Cuban political and revolutionary leader Fidel Castro dies at the age of 90.
2017
- January 21 – 22 – In opposition to Donald Trump's inauguration, millions of people in the US and worldwide join the Women's March.
- January 27 – U.S. President Donald Trump signs an executive order restricting travel and immigration from seven Muslim-majority countries. This order was blocked by the U.S. federal courts; a second, related order issued by Trump was also blocked by the federal courts. The block of second order was partially removed, by the Supreme Court, in June. The Supreme Court stated they would reconsider the order in October.
- March 10 – The UN warns that the world is facing the largest humanitarian crisis since World War II, with up to 20 million people at risk of starvation and famine in Yemen, Somalia, South Sudan and Nigeria.[107]
- March 29 – The United Kingdom triggers Article 50 of the Lisbon Treaty, starting the Brexit negotiations, the talks for the United Kingdom to leave the European Union.[108]
- March 30 – SpaceX conducts the world's first reflight of an orbital-class rocket.[109][110]
- March 31 – Horacio Cartes presents to Congress his plans of allowing the re-election of the president of Paraguay for a second term, going against the Constitution of Paraguay, leading to a political crisis which ended in the storm of Congress by liberal activists and in the assassination of Rodrigo Quintana by the police. After this, the Congress votes against the re-election project.[111]
- October 27 – Catalonia declares independence from Spain,[112] but the declaration is not recognized by the Spanish government or any other sovereign nation.[113]
2018
- February 6 – SpaceX successfully conducts the maiden flight of its most powerful rocket, the Falcon Heavy, from LC39A at John F. Kennedy Space Center in Florida.[114]
- February 9 – 25 – The 2018 Winter Olympics are held in Pyeongchang, South Korea.[115]
- March 11 – The National People's Congress of China approves a constitutional change removing term limits for its leaders, granting Xi Jinping the status of "leader for life". Xi is the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (paramount leader).
- March 19 – Paula-Mae Weekes becomes the first female president of Trinidad and Tobago.
- March 24 – In over 900 cities internationally, people participate in demonstrations against gun violence and mass shootings, calling for stronger gun control in the March for Our Lives, which was a student-led demonstration in response to the Stoneman Douglas High School shooting in Parkland, Florida, that took place in February 14.
- May 9 – The opposition-led Pakatan Harapan coalition, led by former Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad, secures a parliamentary majority in the Malaysian Parliament, ending the 61-year rule of the Barisan Nasional coalition in Malaysia since independence in 1957.
- June 12 – President Donald Trump and North Korean leader Kim Jong-un attend a summit in Singapore, the first meeting between the leaders of the two countries.
- October 28 – Jair Bolsonaro is elected as the 38th president of Brazil, after having been stabbed during the election campaign and undergoing three surgeries.
2019
- January 10 – Venezuela enters a presidential crisis after the disputed results of the 2018 Venezuelan presidential election leads to Juan Guaidó being declared the acting president, disputing Nicolás Maduro.
- February 27 – 28 – President Donald Trump and North Korean leader Kim Jong-un meet for the 2019 North Korea–United States Hanoi Summit in Vietnam.
- March 15:
- Over 2 million people in Hong Kong protest against proposed legislation regarding extradition to China.
- At the first ever Global School Strike for Climate, 1.4 million people in about 2,200 protests across 125 countries gathered urging decision-makers to take responsibility and stop the climate crisis.[116]
- March 23 – Most of the territory formerly held by the Islamic State in Syria collapses amidst the Syrian Civil War. After years of global push back, the extremist group transitions from a proto-state into an insurgency as it retains offshoots and influence in regions across the globe.
- April 11 – Amid mass protests, Omar al-Bashir is deposed as President of Sudan in a coup d'état, after nearly 30 years in office.[117]
- April 21 – A series of Islamist bomb attacks occur at eight locations in Sri Lanka, including three churches, four hotels and one housing complex in Colombo, on Easter Sunday, leaving 259 people dead and over 500 injured. It is the deadliest terrorist attack in the country since the Sri Lankan Civil War ended in 2009.[118]
- April 28 – Victor Vescovo achieves the deepest dive of any human in history, as he reaches Challenger Deep within the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 10,928 m (35,853 ft).[119]
- April 30 – Emperor Akihito of Japan abdicates from his throne, the first abdication by a Japanese monarch in almost two centuries. The abdication ends the Heisei era of Japan and ushers in the Reiwa era with new emperor Naruhito ascending to the throne on May 1.
- July 16 – The European Parliament elects Ursula von der Leyen as the new president of the European Commission.
- September 20 - Likely the largest in world history, the September 2019 climate strikes included protests in 4,500 locations across over 150 countries and gathered roughly 6 million people, many of them schoolchildren.[120]
- December 10 – Sanna Marin, at the age of 34, becomes the world's youngest serving prime minister after being selected to lead Finland's Social Democratic Party.
- December 18 – President Donald Trump is impeached by the United States House of Representatives.
- December 31 – The first known case of COVID-19 is reported in Wuhan, China; the disease would rapidly proliferate into a global pandemic throughout the next three months.[121][122]












2020
- January 2 – The Royal Australian Air Force and Navy are deployed to New South Wales and Victoria to assist mass evacuation efforts amidst the 2019–20 Australian bushfire season.[125][126]
- January 5 – 2019–20 Croatian presidential election – The second round of voting is held and Zoran Milanović of the Social Democratic Party of Croatia defeats incumbent president Kolinda Grabar-Kitarović.[127]
- January 10 – Haitham bin Tariq succeeds Qaboos bin Said as the Sultan of Oman.[128][129]
- January 11 – Presidential and legislative elections are held in Taiwan. Incumbent president Tsai Ing-wen is reelected and the Democratic Progressive Party wins a majority of 67 out of 113 seats in the Legislative Yuan.[130][131][132]
- January 31 – The United Kingdom becomes the first member state to leave the European Union.
- May 26 – Protests break out following the murder of George Floyd across hundreds of cities in the United States and even smaller ones outside the US. Derek Chauvin, the officer responsible for Floyd's murder, would ultimately be convicted on two counts of murder and one of manslaughter in the wake of the protests.
- June 30 – China passes the controversial Hong Kong national security law, allowing China to crack down on opposition to Beijing at home or abroad.
- August 11 – Kamala Harris becomes the Democratic Party's nominee for vice-president of the United States, making her the first African-American, the first Asian-American and the third female vice presidential running mate on a major party ticket.
- August 18 – A mutiny in a military base by soldiers of the Malian Armed Forces develops into a coup d'état. President Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta and Prime Minister Boubou Cissé, among other senior governmental and military officers, are forced to resign.
- August 28 – Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, the longest-serving prime minister in the history of Japan, announces his pending resignation from office, citing ill health, he was replaced by Yoshihide Suga and Fumio Kishida.
- September 4 – Kosovo and Serbia announce that they will normalize economic relations.
- September 29 – The Emir of Kuwait Sheikh Sabah al-Sabah dies at the age of 91. Crown Prince Nawaf Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah is named his successor.
- November 3 – Joe Biden is elected as the 46th president of the United States, and Kamala Harris is elected as vice-president. Biden is the oldest person elected to a first term.
- November 15:
- President of Kyrgyzstan Sooronbay Jeenbekov resigns from office after weeks of massive protests in the wake of the October 2020 parliamentary election; opposition leader Sadyr Japarov assumes office as both the acting president and Prime Minister of Kyrgyzstan.
- The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is signed by 15 Asia-Pacific countries to form the world's largest free-trade bloc, covering a third of the world's population.
2021
- January 1 – The African Continental Free Trade Area comes into effect.[133]
- January 6 – Pro-Trump rioters storm the US Capitol, disrupting the Congressional certification of United States President-elect Joe Biden. Trump is impeached a second time a week later for his role in the storming, making him the first US federal official to be impeached more than once and the first president to have his trial occur after his tenure expired.
- January 20 – Joe Biden and Kamala Harris are inaugurated as the 46th and 49th President and Vice President of the United States. Harris becomes the first Black, South Asian and female Vice President.
- January 22 – The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, the first legally binding international agreement comprehensively to prohibit nuclear weapons, comes into effect.[134]
- January 26 – COVID-19 pandemic: The number of confirmed COVID-19 cases exceeds 100 million worldwide.[135]
- February 1 – A coup d'état in Myanmar removes Aung San Suu Kyi from power and restores military rule.[136]
- February 18 – NASA's Mars 2020 mission (containing the Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter drone) lands on Mars at Jezero Crater, after seven months of travel.[137]
- April 30 – June 13 – A crush during a pilgrimage on Lag BaOmer, renewed violence during the 2021 Israel-Palestine crisis and continuing problems with the COVID-19 pandemic in Israel precede the 2021 Israeli presidential election. Amidst the election, Naftali Bennett and Yair Lapid agree to a rotation government, first headed by Bennett, in order to oust Benjamin Netanyahu as Prime Minister as the month of crises is the culmination of scandals and corruption, including financial criminal charges, during Netanyahu's record long tenure.
- June 7 – The Juno spacecraft performs its only flyby of Jupiter's moon Ganymede, the first flyby of the moon by any spacecraft in over 20 years.[138][139]
- July 7 – President of Haiti, Jovenel Moïse, is assassinated in a midnight attack by unknown mercenaries.
- August 15 – The Taliban regain control of Kabul after US forces and the republican government flee Afghanistan, marking the end of the War in Afghanistan after nearly 20 years.[140]
- November 30 – Barbados becomes a republic by replacing Elizabeth II as Queen with Sandra Mason as president in the role of head of state.
- December 25 – NASA, ESA, the Canadian Space Agency and the Space Telescope Science Institute launch the James Webb Space Telescope, the successor of the Hubble Space Telescope.
2022
- February 4 – 20 – The 2022 Winter Olympics are held in Beijing, China, making it the first city ever to host both the Summer Olympics and Winter Olympics.[141]
- February 24 – After a prolonged military buildup, Russia launches an invasion of Ukraine.
- June 24 – The Supreme Court rules that the Constitution of the United States does not confer a right to abortion, thus overruling the 1973 case Roe v. Wade, and its related 1992 case Planned Parenthood v. Casey. Protests erupt across nearly every major city in the United States.
- July 8 – Former Prime Minister of Japan Shinzo Abe is assassinated while giving a public speech in the city of Nara, Japan.
- September 8 – Elizabeth II, the longest reigning British monarch and longest reigning female monarch dies, and is succeeded by Charles III, her eldest child.
- October 30 – Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva is elected as the 39th president of Brazil, after defeating incumbent Jair Bolsonaro, becoming the first Brazilian president to be elected for a third term.
- November 24 – Long-time opposition leader Anwar Ibrahim is appointed by Yang di-Pertuan Agong Abdullah as Prime Minister of Malaysia.
- December 7 – The Congress of Peru removes President Pedro Castillo from office and arrests him after he tries to dissolve congress in a coup attempt, Vice President Dina Boluarte succeeds him, leading to large protests against Boluarte and in favor of Castillo to erupt.
- December 19 – At the UN Biodiversity Conference (COP15), nearly 200 countries agree a landmark deal to protect a third of the planet for nature by 2030.[142][143]
- December 29 – Brazilian football legend Pelé dies at the age of 82.[144]
- December 31 – Pope Emeritus Benedict XVI, who served from 2005 until his resignation in 2013, dies at the age of 95.
2023
- January 1 – Croatia adopts the euro and joins the Schengen Area, becoming the 20th member state of the Eurozone and the 27th member of the Schengen Area. This is the first enlargement of the Eurozone since Lithuania's entry in 2015, and the first enlargement of the Schengen Area since Liechtenstein's entry in 2011.[145][146]
- February 6 – Two earthquakes strike southern Turkey, the first 7.8 (Mww) in Gaziantep Province and the other 7.5 Mww in Kahramanmaraş Province, causing widespread damage and at least 58,000 deaths in Turkey and Syria, with more than 120,000 injured.[147][148]
- February 27 – The United Kingdom and the European Union reach a new agreement surrounding modifications to the Northern Ireland Protocol.
- March 10 – The National People's Congress unanimously re-elects Xi Jinping as the President of the People's Republic of China to an unprecedented third term.
- March 17 – The International Criminal Court issues an arrest warrant for Russian president Vladimir Putin, the first against a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council.
- April 4 – Finland becomes the 31st member of NATO, doubling its border with Russia.
- April 14 – Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) is launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) to search for life in the Jovian system, with an expected arrival date of 2031.
- May 5 – World Health Organization declares end of the COVID-19 pandemic global health emergency.
- May 6: The coronation of Charles III and Camilla as King and Queen of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms is held in Westminster Abbey, London.
- June 14: Scientists report the creation of the first synthetic human embryo from stem cells, without the need for sperm or egg cells.
- June 19: The United Nations General Assembly unanimously adopts the High Seas Treaty, the first treaty aimed towards marine conservation in international waters.
- June 23 – The Wagner group launches a rebellion against the Russian government.
- July 14 – SAG-AFTRA announces it will begin an ongoing strike against the major film and TV studios in protest of low compensation, ownership of work, and generative AI.
- August 18 – The United States, Japan, and South Korea agree to sign a trilateral pact.
- August 23:
- India's Chandrayaan-3 becomes the first spacecraft to land near the south pole of the Moon.
- Wagner Group leader Yevgeny Prigozhin and founder Dmitry Utkin are killed when their plane crashes outside of Moscow, killing eight others.
- August 30 – In the hours following the announcement of incumbent president Ali Bongo Ondimba's reelection as President of Gabon after the 2023 presidential election, the military launches a successful coup d'état and creates the Committee for the Transition and Restoration of Institutions to govern the country, ending the rule of the Bongo family after 56 years in power.
- September 9 – At the 18th G20 summit in New Delhi, the African Union is announced as the 21st permanent member of the G20.
- September 10 – Storm Daniel, a Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone makes landfall in Libya, killing at least 5,000 people, with Libyan authorities announcing between 10,000 and 100,000 missing. In the city of Derna in Libya, two dams collapsed, resulting in a quarter of the city being destroyed.
- September 28 – President of Artsakh Samvel Shahramanyan signs a decree that will dissolve all state institutions of Artsakh by 1 January 2024, bringing an end to the breakaway state.
- October 7:
- Hamas militants launch a large-scale attack from the Gaza Strip, infiltrating southern Israel and prompting a full military response from the Israel Defense Forces.
- A doublet earthquake occurs in Herat Province in Afghanistan, killing 2,000 people and injuring over 9,000, with tremors felt in Iran and Turkmenistan. The earthquake is the deadliest in the country since 1998.
- October 8 – Israel's Security Cabinet formally declares war, for the first time since the Yom Kippur War in 1973, on Hamas.
- October 15 – Twenty-one species in the United States are declared extinct by the US Fish and Wildlife Service. These are one mammal, ten birds, two fish, and eight mussels.
- November 1 – The first AI Safety Summit takes place in the United Kingdom, with 28 countries signing a "world first agreement" on how to manage the riskiest forms of artificial intelligence.
- November 9:
- U.S. surgeons at NYU Langone Health announce the world's first whole eye transplant.
- SAG-AFTRA ends its strike at 12:01 a.m. PDT following a tentative deal reached the day prior.
- November 24 – Somalia is admitted as the eighth member of the East African Community, having applied for membership in 2012.
- December 6 – Google DeepMind releases the Gemini Language Model. Gemini will act as a foundational model integrated into Google's existing tools, including search and Bard.
- December 12 – At the COP28 climate summit in Dubai, a consensus is reached for countries to "transition away" from fossil fuels, the first such agreement in the conference's 30-year history.
- December 16 – Emir of Kuwait Nawaf Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah dies at the age of 86 and is succeeded by his half-brother Mishal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah.
2024
- January 1:
- Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates become BRICS members.
- The Republic of Artsakh is formally dissolved as Nagorno-Karabakh unifies with Azerbaijan.
- Ethiopia announces an agreement with Somaliland to use the port of Berbera. Ethiopia also says that it will eventually recognize Somaliland's independence, becoming the first country to do so.
- Disney's copyright protection on Steamboat Willie and the original Mickey Mouse expires as they enter the public domain.
- January 8:
- Astrobotic Technology alongside NASA launch the first commercial Lunar Lander. Seven hours after launch, an anomaly prevents stable orientation due to propulsion issues, resulting in critical fuel loss and the abandonment of the moon landing.
- Ecuadorian President Daniel Noboa declares a state of emergency following the escape of Los Choneros drug cartel leader José Adolfo Macías Villamar, from prison.
- January 13 – 2024 Taiwanese Presidential Election: Lai Ching-te of the ruling Democratic Progressive Party wins with 40% of the votes.
- January 14:
- Queen Margrethe II of Denmark formally abdicates as Queen on the 52nd anniversary of her accession, with her eldest son Frederik succeeding her as King Frederik X.
- 2024 Comorian Presidential Election: Amid an opposition boycott, incumbent president Azali Assoumani wins re-election with 62.9% of the vote and only 16.3% voter turnout.
- January 15: Following a brief political crisis in the aftermath of the 2023 elections, Bernardo Arévalo is inaugurated as the 52nd President of Guatemala.
- January 19: Japan becomes the fifth country to successfully soft land on the Moon, with its SLIM mission.
- January 26 – 2024 Tuvaluan general election: Kausea Natano, the incumbent Prime Minister of Tuvalu, loses reelection to Parliament. A month later, Feleti Teo is elected prime minister.
- February 4:
- President of Namibia Hage Geingob dies at the age of 82, and is succeeded by his vice-president Nangolo Mbumba.[149][150]
- 2024 Salvadoran general election: Incumbent President Nayib Bukele wins the election with over 80% of the vote, becoming the first president to be reelected in El Salvador since 1944.[151][152]
- February 6 – Former President of Chile Sebastián Piñera dies in a helicopter crash at the age of 74.[153]
- February 7 – 2024 Azerbaijani presidential election: Amid an opposition boycott, President Ilham Aliyev is reelected to a fifth term.[154]
- February 8 – 2024 Pakistani general election: Independent politicians, most of whom are members of the banned political party Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf, win a plurality of seats in the National Assembly.[155]
- March 7 – Sweden officially joins NATO, becoming its 32nd member.[156][157]
- March 10 – 2024 Portuguese legislative election: The Democratic Alliance wins a plurality of seats and forms a minority government amid losses by the incumbent Socialist Party and major gains by the right-wing Chega party.[158][159]
- March 11 – Haitian acting Prime Minister and President Ariel Henry announces his pending resignation from both offices amid an ongoing crisis marked by gang warfare in the country.[160]
- March 13 – The Artificial Intelligence Act, the world's first comprehensive legal and regulatory framework for artificial intelligence, is passed by the European Union.[161]
Politics, wars and states


New countries and territorial changes
Some territories and states have gained independence during the 21st century. This is a list of sovereign states that have gained independence in the 21st century and have been recognized by the UN.

 East Timor (Timor-Leste)[162] on 20 May 2002.
East Timor (Timor-Leste)[162] on 20 May 2002. Montenegro on 3 June 2006.
Montenegro on 3 June 2006. Serbia on 3 June 2006.
Serbia on 3 June 2006.-
 South Sudan on 9 July 2011.
South Sudan on 9 July 2011.
These nations gained sovereignty through government reform.
 Comoros on 23 December 2001.
Comoros on 23 December 2001.
The Union of the Comoros replaced the Federal Islamic Republic of the Comoros
 Transitional Islamic State of Afghanistan on 13 July 2002.
Transitional Islamic State of Afghanistan on 13 July 2002.
The Transitional Islamic State of Afghanistan replaced the Islamic State of Afghanistan.
 State Union of Serbia and Montenegro on 4 February 2003.
State Union of Serbia and Montenegro on 4 February 2003.
The State Union of Serbia and Montenegro replaced the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
 Islamic Republic of Afghanistan on 7 December 2004.
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan on 7 December 2004.
The Islamic Republic of Afghanistan replaced the Transitional Islamic State of Afghanistan
 Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal on 28 May 2008.
Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal on 28 May 2008.
The Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal replaced the Kingdom of Nepal.
 National Transitional Council of Libya on 20 October 2011.
National Transitional Council of Libya on 20 October 2011.
The National Transitional Council of Libya replaced the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya.
 State of Libya on 8 August 2012.
State of Libya on 8 August 2012.
The State of Libya replaced the National Transitional Council of Libya.
 Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan on 15 August 2021.
Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan on 15 August 2021.
The Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan replaced the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan.
These territories have declared independence and secured relative autonomy but they have only been recognized by some UN member states:
 Kosovo on 17 February 2008. (partially recognized)
Kosovo on 17 February 2008. (partially recognized) South Ossetia on 26 August 2008. (partially recognized)
South Ossetia on 26 August 2008. (partially recognized) Abkhazia on 26 August 2008. (partially recognized)
Abkhazia on 26 August 2008. (partially recognized)
These territories have declared independence and secured relative autonomy but they have been recognized by no one:
 Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in June 2014. Had taken over much of Iraq, Syria and Libya. It is considered a terrorist organization and no longer holds any significant territorial control.
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in June 2014. Had taken over much of Iraq, Syria and Libya. It is considered a terrorist organization and no longer holds any significant territorial control. Republic of Catalonia on 27 October 2017. The Catalan Parliament proclaimed the Catalan Republic, but the Kingdom of Spain did not recognise this and for a time imposed direct rule. (See 2017 Catalan independence referendum and 2017–2018 Spanish constitutional crisis)
Republic of Catalonia on 27 October 2017. The Catalan Parliament proclaimed the Catalan Republic, but the Kingdom of Spain did not recognise this and for a time imposed direct rule. (See 2017 Catalan independence referendum and 2017–2018 Spanish constitutional crisis) Southern Transitional Council in March 2017. Claimed the majority of the southern part of Yemen and the restoration of South Yemen.
Southern Transitional Council in March 2017. Claimed the majority of the southern part of Yemen and the restoration of South Yemen.
These territories were annexed from a sovereign country, the action has only been recognized by some UN member states:
 Crimea annexed from Ukraine into the Russian Federation on 18 March 2014.
Crimea annexed from Ukraine into the Russian Federation on 18 March 2014. Donetsk People's Republic,[b]
Donetsk People's Republic,[b]  Kherson Oblast,
Kherson Oblast,  Luhansk People's Republic,[c] and
Luhansk People's Republic,[c] and  Zaporizhzhia Oblast annexed from Ukraine into the Russian Federation on 30 September 2022.
Zaporizhzhia Oblast annexed from Ukraine into the Russian Federation on 30 September 2022.
These territories were ceded to another country:

 India–Bangladesh enclaves, traded between the two countries in 2015.
India–Bangladesh enclaves, traded between the two countries in 2015. Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh and the Lachin corridor, ceded by Armenia to Azerbaijan on 1 January 2024.
Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh and the Lachin corridor, ceded by Armenia to Azerbaijan on 1 January 2024.
Science and technology
Space exploration


- 2001 – Dennis Tito becomes the first space tourist by paying $19 million to board the International Space Station.
- 2003 – Space Shuttle Columbia disaster on 1 February.
- 2003 – The Chinese space program launches its first crewed space flight, Shenzhou 5, on 15 October. This made China the third country in the world to have indigenous crewed space capability.
- 2004 – Mars Exploration Rovers Spirit and Opportunity land on Mars; Opportunity discovers evidence that an area of Mars was once covered in water.
- 2004 – SpaceShipOne makes the first privately funded human spaceflight, on 21 June.
- 2005 – The Huygens probe lands on Titan, the largest of Saturn's moons, on 14 January.
- 2006 – The New Horizons probe is launched to Pluto, on 19 January.
- 2006 – Pluto is reclassified from a planet to a dwarf planet, leaving the solar system with eight planets.
- 2007 – China launches its first lunar mission with the Chang'e 1, on 24 October.
- 2008 – India launches its first lunar mission Chandrayaan-1 which included a remote sensing orbiter and impactor on 22 October 2008. It made India the third nation to place its flag on Moon.
- 2008 – Chinese space program launches its third crewed space flight carrying its first three-person crew and conducts its first spacewalk that makes China the third nation after Russia and USA to do that, Shenzhou 7, on 25 September.
- 2008 – Phoenix discovers water ice on Mars.
- 2009 – Iran launches its first satellite, Omid, on 2 February.
- 2011 – NASA retires the last Space Shuttle, Atlantis, marking an end to its three-decade shuttle program.
- 2012 – SpaceX successfully delivers cargo to the International Space Station.
- 2012 – NASA successfully lands the Curiosity rover on the surface of Mars, on 6 August.
- 2014 – India's Mars Orbiter Mission, the nation's first attempt to send a spacecraft to Mars, successfully entered orbit on 24 September, making India the fourth nation in the world to reach that goal.
- 2014 – The European Space Agency robotic spacecraft Philae landed successfully on the comet 67P, the first cometary landing ever.
- 2015 – On 14 July, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft became the first to fly by Pluto, on a mission to photograph and collect data on its planetary system. No other spacecraft has yet performed such a mission so far from Earth.
- 2015 – On 28 September, NASA announces that liquid water has been found on Mars.[163]
- 2015 – SpaceX launches and lands a Falcon 9 into orbital space on 21 December, becoming the first reusable rocket to do so.
- 2016 – SpaceX lands the first orbital rocket, a CRS-8, on a drone platform at sea on 8 April.
- 2016 – On 4 July, NASA's Juno space probe maneuvered into a polar orbit to study the planet Jupiter.[164]
- 2016 – On 26 July, Solar Impulse 2 becomes the first solar-powered aircraft to circumnavigate the world.
- 2016 – On 24 August, an Earth-sized exoplanet is discovered around Proxima Centauri, 4.2 light years away, which is potentially habitable.
- 2016 – On 8 September, NASA's ORIRIS-Rex space probe is launched as the first asteroid sample return mission to collect samples from Bennu.
- 2019 – On 3 January, Chinese probe Chang'e 4 becomes the first human-made object to land on the far side of the Moon.[165]
- 2019 – NASA concludes the 15-year Opportunity rover mission after being unable to wake the rover from hibernation.[166]
- 2019 – Israel launched its first spacecraft, Beresheet, towards the Moon on 7 April; after two months of journey, the spacecraft failed to land and crashed on the surface of the Moon, making Israel the seventh country to orbit the Moon.
- 2019 – The first image of the supermassive black hole inside galaxy Messier 87 was captured by the Event Horizon Telescope.[167]
- 2021 – NASA's Perseverance rover, carrying the Ingenuity helicopter, successfully lands on Mars.
- 2021 – NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is successfully launched into orbit.
- 2022 – The first image of the supermassive black hole inside Milky Way was captured by the Event Horizon Telescope.
- 2022 – The first image from the James Webb Space Telescope is published.[168]
- 2022 – NASA successfully launches the Artemis 1 Moon mission on the SLS spacecraft after multiple delays.
- 2023 – India successfully touched down near the south pole of the Moon with Chandrayaan-3's lander on August 23, making it only the fourth country to achieve the feat of reaching lunar surface after the US, China and the erstwhile Soviet Union.[169]
Physics
- 2003 – WMAP observations of the cosmic microwave background.
- 2010 – The Large Hadron Collider's first high energy collisions took place in March 2010.
- 2012 – Physicists discover the Higgs boson based on collisions at the Large Hadron Collider, on 4 July. It is the latest particle to be discovered in the Standard Model.[170]
- 2016 – On 11 February, LIGO announces the discovery of bursts of gravitational waves generated by cosmic collisions of black holes on, and was previously predicted by Albert Einstein 100 years ago.
- 2022 – on 13 December, the US Department of Energy announces that scientists at the National Ignition Facility have achieved the first positive energy gain from a fusion reactor in history.[171]
Mathematics
- 2002 – Grigori Perelman posted the first of a series of eprints to the arXiv, in which he proved the Poincaré conjecture, the first of the Millennium Prize Problems to be solved.
- 2013 – Yitang Zhang publishes a paper in the Annals of Mathematics that established the first finite bound on the least gap between consecutive primes that is attained infinitely often.
Meteorology
- 2005 – A record 27 named storms occurred during the Atlantic hurricane season. The National Hurricane Center runs out of names from its standard list and uses Greek alphabet for the first time.[172][173]
- 2007 – The Enhanced Fujita scale is formally released and put into use across the United States, replacing the Fujita scale.[174][175]
- 2013:
- Environment Canada (EC) adopts a variation of the Enhanced Fujita scale (CEF-scale), replacing the Fujita scale across Canada.[176]
- A violent EF5 tornado impacts Moore, Oklahoma, marking the last tornado to receive the rating of EF5 on the Enhanced Fujita scale.[177]
- A violent tornado impacts areas around El Reno, Oklahoma.[178] The University of Oklahoma's RaXPol mobile Doppler weather radar, positioned at a nearby overpass, measured winds preliminarily analyzed as in excess of 296 mph (476 km/h). These winds are considered the second-highest ever measured worldwide, just shy of the 302 ± 22 mph (486 ± 35 km/h) recorded during the 1999 Bridge Creek–Moore tornado.[179][180]
- 2015 – The European Severe Storms Laboratory along with the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics publish a detailed assessment of the 1764 Woldegk tornado, in which it was assigned a rating of F5 on the Fujita scale, marking the oldest official F5 tornado.[181]
- 2023:
- Elizabeth Leitman becomes the first woman to issue a convective watch from the Storm Prediction Center.[182][183][184]
- The TORNADO Act was introduced by U.S. Senator Roger Wicker as well as eight other senators from the 118th United States Congress.[185]
- The International Fujita scale (IF-scale) is officially published.[186]
- 2024 – Researchers with the University of Tennessee and University of Missouri publish an academic study about how survivors from the 2011 Joplin tornado recover from "Tornado Brain", a new term for the PTSD of tornado survivors.[187]
Biotechnology and medicine
- 2001 – The first telesurgery is performed by Jacques Marescaux.
- 2003 – Completion of the Human Genome Project
- 2005 – The first successful partial face transplant is performed in France.
- 2006 – Australian of the Year Dr Ian Frazer develops a vaccine for cervical cancer.
- 2007 – Visual prosthetic (bionic eye) Argus II.
- 2008 – Japanese scientists create a form of artificial DNA.
- 2008 – Laurent Lantieri performs the first full face transplant.
- 2011 – First successful Uterus transplant from a deceased donor in Turkey.
- 2012 – The first successful complete face transplant is performed in Turkey.
- 2012 – Doubts raised over Statin medication.
- 2013 – First kidney grown in vitro in the U.S.
- 2013 – First human liver grown from stem cells in Japan.
- 2014 – A 3D printer is used for first ever skull transplant.[188]
- 2016 – The first ever artificial pancreas is created.[189]
- 2019 – Researchers 3D-print a heart from human patient's cells.[190]
- 2020 – First COVID-19 Vaccine is developed.
- 2022 – The complete human genome is sequenced.[191]
Telecommunications
The Digital Revolution continued into the early 21st century with mobile phone usage and Global Internet usage growing massively, becoming available to many more people, with more applications and faster speeds.
|
Social networking emerged in the mid-2000s as a popular form of social communication, partly replacing much of the function of email, message boards and instant messaging services. Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, Snapchat and WeChat are all major examples of social media which have gained widespread popularity. The use of webcams and front-facing cameras on PCs and related devices, and services such as Skype, Zoom and FaceTime, have made video calling and video conferencing widespread. Their use hugely increased during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Civil unrest








- Second Intifada
- 2001 Harehills riot
- 2001 G8 Genoa summit protests
- December 2001 riots in Argentina
- 2002 Gujarat riots
- Protests against the Iraq War
- Bolivian gas conflict
- 2003 Maldives civil unrest
- Rose Revolution
- 2004 Venezuelan protests
- 2004 Qamishli riots
- 2004 unrest in Kosovo
- 2004 Dublin May Day protests
- Orange Revolution
- Tulip Revolution
- Cedar Revolution
- 2005 Belize unrest
- Protests against Faure Gnassingbé
- 2005 Belfast riots
- 2005 civil unrest in France
- 2005 Cronulla riots
- Jeans Revolution
- 2006–2008 Lebanese protests
- Saffron Revolution
- 2007 Georgian demonstrations
- 2008 Armenian presidential election protests
- 2008 Tibetan unrest
- 2008 riot in Mongolia
- 2009 Icelandic financial crisis protests
- 2009 G-20 London summit protests
- April 2009 Moldovan parliamentary election protests
- 2009–2010 Iranian election protests
- July 2009 Ürümqi riots
- 2010 Thai political protests
- Kyrgyz Revolution of 2010
- 2010 Kingston unrest
- 2010 G-20 Toronto summit protests
- 2010 Mozambican protests
- 2010 UK student protests
- 2010–2012 Greek protests
- Arab Spring
- Tunisian revolution
- 2011 Egyptian revolution
- 2011 Egyptian Post-Revolution protests
- Impact of the Arab Spring
- 2011 Magallanes protests
- 2011 Iranian protests
- 2011 Libyan civil war
- Syrian civil war
- 2011 Northern Ireland riots
- 2011 Malawian protests
- 2011 United Kingdom anti-austerity protests
- Anti-austerity movement in Portugal
- Spanish "Indignants"
- 2011 England riots
- 2011–13 Chilean student protests
- 2011 Israeli social justice protests
- Worldwide "Occupy" Protests
- 2011–2013 Russian protests
- Bersih 3.0 rally
- Yo Soy 132
- Belfast City Hall flag protests
- 2012–2013 Iraqi protests
- 2013 Myanmar anti-Muslim riots
- Gezi Park protests
- 2013 protests in Brazil
- June 2013 Egyptian protests
- 2013 Bangladesh quota reform movement
- 2013–2014 Cambodian protests
- 2013 Muzaffarnagar riots
- 2013–2014 Thai political crisis
- Euromaidan
- 2013 Italian social protests
- 2013 Little India riots
- 2014 Ukrainian Revolution
- 2014 pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine
- 2014 unrest in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Venezuelan protests (2014–present)
- 2014 anti-Muslim riots in Sri Lanka
- 2014 Pakistan anti-government protest
- 2014 Ferguson unrest
- 2014 Hong Kong protests
- 2015 Baltimore protests
- Burundian unrest (2015–2018)
- 2015–18 Iraqi protests
- 2015 Lebanese protests
- Protests against Donald Trump
- FeesMustFall
- Nuit debout
- 2016 Gabonese protests
- 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt
- 2016–17 South Korean protests
- Dakota Access Pipeline protests
- 2016 Manipur unrest
- 2016–17 Cameroonian protests
- 2017–2019 Romanian protests
- 2017 Belarusian protests
- 2017–2018 Russian protests
- 2017–2018 Spanish constitutional crisis
- Unite the Right rally
- 2017–2018 Honduran protests
- 2018 Bangladesh quota reform movement
- 2018 anti-Muslim riots in Sri Lanka
- 2018–2019 Nicaraguan protests
- 2018 Bangladesh road-safety protests
- Yellow vests movement
- Serbian protests (2018–present)
- Sudanese Revolution
- 2018 Armenian revolution
- 2018–2023 Haitian crisis
- 2019–2020 Algerian protests
- 2019–20 Hong Kong protests
- 2019 Venezuelan uprising attempt
- 2019 Papua protests
- 2019 Egyptian protests
- 2019–2020 Iraqi protests
- 2019 Ecuadorian protests
- 2019–2020 Chilean protests
- 2019 Catalan protests
- 2019–2020 Guinean protests
- 2019–20 Lebanese protests
- 2019 Bolivian protests
- 2019 Indonesian protests and riots
- 2019–20 Iranian protests
- 2019 Maltese protests
- 2019-2020 Colombian protests
- Citizenship Amendment Act protests
- 2020–2021 Thai protests
- 2020–2021 protests against Benjamin Netanyahu
- United States racial unrest (2020–2023)
- 2020 Belarusian protests
- 2020–2021 Serbian protests
- 2020–2021 Bulgarian protests
- 2020–2021 Indian farmers' protest
- End SARS protests
- 2020 Polish protests
- 2020 Peruvian protests
- 2020–2021 United States election protests
- 2020–2021 Armenian protests
- 2020 Guatemalan protests
- 2021 Dutch curfew riots
- 2021 Russian protests
- 2021 Myanmar protests
- 2021 Senegalese protests
- 2021 Paraguayan protests
- 2021 Colombian protests
- 2021 South African unrest
- 2022 Kazakh protests
- 2022 Sri Lankan protests
- 2022 Ecuadorian protests
- Anti-MONUSCO protests
- 2022 Sierra Leone protests
- Mahsa Amini protests
- 2022–2023 Brazilian election protests
- 2022 Mongolian protests
- 2022–2023 Peruvian protests
- 2023 Israeli judicial reform protests
- 2023 French pension reform strikes
- 2023 Pakistani protests
- 2023 South African National Shutdown
- 2023 Manipur violence
- 2023 Senegalese protests
- Nahel Merzouk protests
- 2023 Armenian protests
- 2024 European farmers' protests
- 2024 Papua New Guinean unrest
- 2024 Indian farmers' protest
- 2024 pro-Palestinian protests on university campuses
- 2024 New Caledonia unrest
- 2024 Bangladesh quota reform movement
- Kenya Finance Bill protests
- 2024 Harehills unrest
- 2024 United Kingdom riots
- End Bad Governance protests
- 2024 Indonesian local election law protests
Disasters
Natural disasters


2000s
- 2001 Gujarat earthquake – An earthquake in Gujarat, India on 26 January 2001, killed approximately 20,000 people.
- January 2001 El Salvador earthquake – A 7.9 earthquake in El Salvador shook the whole country on 13 January 2001, causing a major devastating landslide, hundreds dead, thousands injured and many homeless. A month later, on 13 February 2001, the country suffered a second earthquake – 6.7
- 2003 European heat wave – Approximately up to 70,000 people were killed across Europe in a summer long heat wave.
- 2003 Bam earthquake – An earthquake in Bam, Iran on 27 December 2003, killed more than 26,000.
- 2004 Hurricane Jeanne – Over 3,000 people are killed by Hurricane Jeanne in Haiti in September 2004.
- 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami – On 26 December 2004, a massive undersea earthquake resulted in a massive tsunami striking southeast Asia killing approximately 230,000.
- 2005 Hurricane Katrina – The hurricane killed 1,836 in southeast Louisiana and Mississippi (mostly in New Orleans) and South Florida. A significant portion of the city, most of which sits below sea level, was submerged. Damages reached US$81.5 billion, making Katrina the costliest tropical cyclone ever recorded in the U.S.
- 2005 Kashmir earthquake – An earthquake in Kashmir on 8 October 2005, killed at least 74,500 in India and Pakistan.
- 2008 Cyclone Nargis – lead to catastrophic storm surge, leading to a death toll in excess of 100,000 and making millions homeless.
- 2008 Sichuan earthquake – An earthquake between 7.9 and 8.0-magnitude struck Sichuan, China, on 12 May 2008, killing 68,712, with 17,921 missing.
- 2009 Black Saturday bushfires – The Black Saturday bushfires were a series of bushfires that ignited or were burning across the Australian state of Victoria, Australia on and around Saturday, 7 February 2009. The fires occurred during extreme bushfire-weather conditions and resulted in Australia's highest ever loss of life from a bushfire; 173 people died and 414 were injured.
- 2009 L'Aquila earthquake – A 6.3 magnitude earthquake strikes near L'Aquila (Italy) on 6 April 2009, one of the worst in Italian history. 308 were pronounced dead and more than 65,000 were made homeless.
- 2009 flu pandemic – A worldwide outbreak of Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 spread around the world forming a pandemic by June 2009.
2010s


- 2010 Haiti earthquake – At least 230,000 are killed in Haiti after a massive earthquake on 12 January 2010. Three million people were made homeless.
- 2010 Chile earthquake – A massive earthquake, magnitude 8.8, strikes the central Chilean coast on 27 February 2010.
- 2010 Yushu earthquake – A large 6.9 magnitude earthquake struck the Yushu region of China in Qinghai near Tibet, on 14 April 2010, killing over 2,200 people.
- 2010 eruption of Eyjafjallajökull – A massive ash cloud is formed by the eruption of the Icelandic volcano Eyjafjallajökull, on 14 April 2010, grounding flights across northwest Europe. Scientists began recording volcanic activity there in 2009 which increased through March 2010 culminating in the second phase eruption in April.
- 2010 Pakistan floods – Began in July 2010 after record heavy monsoon rains. The Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan was worst affected. At least 1,600 people were killed, thousands were rendered homeless, and more than thirteen million people were affected.[194][195][196][197][198] Estimates from rescue service officials suggest the death toll may reach 3,000 victims.[199]
- 2011 Queensland floods – Began in December 2010 primarily in Queensland. The flood causes thousands of people to evacuate. At least 200,000 people were affected by the flood. The flood continued throughout January 2011 in Queensland, and the estimated reduction in Australia's GDP is about A$30 billion.
- Cyclone Yasi – A category 5 (Australian Scale) cyclone hits North Queensland with winds as strong as 290 km/h (197 miles/hr) and devastates the residents of North Queensland.
- February 2011 Christchurch earthquake – 185 people died in New Zealand after a 6.3-magnitude earthquake hit Christchurch on 22 February 2011, making it New Zealand's second-deadliest natural disaster after the 1931 Hawke's Bay earthquake.
- 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami – On 11 March 2011, a catastrophic undersea earthquake of magnitude 9.0 occurred offshore of eastern Japan, the greatest in the country's history and created a massive tsunami which killed 15,894; it also triggered the Fukushima I nuclear accidents. The overall cost for the earthquake, tsunami and nuclear accidents reached up to US$235 billion, making it the costliest natural disaster on record.
- 2011 Super Outbreak – Regarded as the deadliest tornado outbreak ever recorded and dubbed the 2011 Super Outbreak, a catastrophic tornado outbreak on 25–28 April affected the Southern United States and killed over 330 people, most of whom were in or from Alabama. Damages are expected to be near or over $10 billion.
- 2011 Joplin tornado – On 22 May 2011, a devastating EF5 tornado struck Joplin, Missouri, resulting in 159 casualties, making it the deadliest tornado to hit the United States since 1947.
- Tropical Storm Washi – Locally known as Sendong, it caused catastrophic flooding in the Philippine island of Mindanao on the night of 16 December 2011. The hardest hits were in Cagayan de Oro and Iligan City. Almost 1000 people perished, most of whom were sleeping, and President Benigno Aquino III declared a state of calamity four days later.
- Hurricane Sandy – 24–30 October 2012 – kills at least 185 people in the Caribbean, Bahamas, United States and Canada. Considerable storm surge damage causes major disruption to the eastern seaboard of the United States.[200][201][202]
- 2013 Bohol earthquake – An earthquake of magnitude 7.2 that killed 22 people and destroyed a total worth of ₱2.25 billion,
- Typhoon Haiyan 2013 – kills more than 6,000 people in central Philippines. Considered to be one of the strongest storms ever, it brought major damage and loss of life to the Philippines, especially the islands of Leyte and Samar. A worldwide humanitarian effort began in the aftermath of the typhoon.
- 2014 Southeast Europe floods – kill at least 80 people in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. Floodwaters caused over 2,000 landslides across the Balkan region, spreading damage across many towns and villages.
- April 2015 Nepal earthquake – An earthquake of 7.8 magnitude kills almost 9,000 people, injures another 22,000 and leaves nearly 3 million people homeless in Central Nepal. The earthquake was so strong it was felt in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh.
- 2016 Taiwan earthquake – An earthquake of 6.4 magnitude kills 117 people, injures 550, and 4 people were left missing. The earthquake resulted in 3 executives of the Weiguan developer being arrested under charges of professional negligence resulting in death.
- August 2016 Central Italy earthquake – A 6.2 magnitude earthquake killed 299 people and severely damaged Amatrice, Accumoli and Arquata del Tronto.
2020s
- Unprecedented flooding displaces millions and threatens famine in Sudan and South Sudan in 2020–2021.[203][204]
- On 12 January 2020, the Taal Volcano erupted for the first time in 43 years.
- The 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, the most active regional season on record with 30 total named storms, results in over 400 fatalities across parts of the United States, Central America and the Caribbean.
- At least 20 people are killed in 2021 Henan floods in China after heavy rainfall (at least 20c per hour) exacerbated by the approach of Typhoon In-fa breaks existing records.
- The 2021 European floods kill over 188 people and devastate Belgium, Germany, Austria, the Netherlands, Croatia, Switzerland, Italy and Luxemburg. Floods in Germany prove to be the deadliest since the North Sea Flood of 1962.
- On 27 July 2022, a magnitude-7.0 earthquake hit Luzon, causing 11 deaths and ₱1.88 billion of property damage.
- In September 2022, Hurricane Ian hit the west coast of Florida as a Category 4 Atlantic hurricane, becoming the deadliest hurricane to hit Florida since the 1935 Labor Day hurricane.
Human-made disasters

- On 27 July 2002, a Sukhoi Su-27 fighter crashes at an air show in Ukraine, killing 77 and injuring more than 100, making it the worst air show disaster in history.
- On 1 February 2003, at the conclusion of the STS-107 mission, the Space Shuttle Columbia disintegrates during reentry over Texas, killing all seven astronauts on board.
- The Black Saturday bushfires – the deadliest bushfires in Australian history took place across the Australian state of Victoria on 7 February 2009, during extreme bushfire-weather conditions, resulting in 173 people killed, more than 500 injured, and around 7,500 homeless. The fires came after Melbourne recorded the highest-ever temperature (46.4 °C, 115 °F) of any capital city in Australia. The majority of the fires were ignited by either fallen or clashing power lines or deliberately lit.
- On 10 April 2010, Polish President Lech Kaczyński, his wife and 94 other people, including dozens of government officials, are killed in a plane crash.
- On 20 April 2010, an explosion on the Deepwater Horizon offshore drilling rig, operating in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Louisiana, left eleven crewmen dead and resulted in a fire that sank the rig and caused a massive-scale oil spill[205] that may become one of the worst environmental disasters in United States history.[206] On 18 June 2010, oceanographer John Kessler said that the crude gushing from the well contains 40 percent methane, compared to about 5 percent found in typical oil deposits. Methane is a natural gas that could potentially suffocate marine life and create "dead zones" where oxygen is so depleted that nothing lives. "This is the most vigorous methane eruption in modern human history," Kessler said.[207] On 20 June an internal BP document was released by Congress revealing that BP estimated the flow could be as much as 100,000 barrels (4,200,000 US gallons; 16,000 cubic metres) per day under the circumstances that existed since 20 April blowout.[208][209]
Pandemics and epidemics


- 2002–2004 – Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) spreads to many countries in the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak, causing 774 deaths.
- 2009 – Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 spreads around the world, becoming a global pandemic, with over 200,000 deaths.
- 2013–2016 – Ebola virus spreads in west Africa, causing over 11,000 deaths.
- 2020–2023 – A worldwide pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus takes place. It leads to widespread social and economic disruption and more than 7 million reported deaths.[11] However, it is estimated that around 18.2 to 33.5 million people may have died in the Pandemic.[12]
- 2022–2023 – Mpox spreads to many countries around the world in the 2022–2023 mpox outbreak, causing 207 deaths.
Economics and industry
- The 2007–2008 financial crisis led to the Great Recession.
- In the early 2010s the European debt crisis caused major effects on European politics and contributing to power shifts and the introduction of austerity policies in different countries.
- Developing countries make up for 97% of the world's growth, and industrialization leads to the rapid rise of BRICS economies and the weakening of American hegemony in the global economy.
- The recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic forced many governments and economic sectors to heavily invest and restructure, especially through widespread introduction of remote work.
- Economic restructuring was pursued in many economies due to global climate change.
Sports
Association football is the most popular sport worldwide with the FIFA World Cup being the most viewed football event. Other sports such as rugby, cricket, baseball, basketball, ice hockey, tennis, and golf are popular globally. In cricket, the emergence of the Twenty20 format and the creation of the Indian Premier League led to changes in the nature of the sport. American swimmer Michael Phelps won an Olympic record setting 8 Gold medals at the 2008 Summer Olympics.

Olympics
- The 2002 Winter Olympics were held in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States
- The 2004 Summer Olympics were held in Athens, Greece
- The 2006 Winter Olympics were held in Turin, Italy
- The 2008 Summer Olympics were held in Beijing, China
- The 2010 Winter Olympics were held in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
- The 2012 Summer Olympics were held in London, United Kingdom
- The 2014 Winter Olympics were held in Sochi, Russia
- The 2016 Summer Olympics were held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
- The 2018 Winter Olympics were held in Pyeongchang, South Korea
- The 2020 Summer Olympics were held in Tokyo, Japan
- The 2022 Winter Olympics were held in Beijing, China
- The 2024 Summer Olympics were held in Paris, France
- The 2026 Winter Olympics will be held in Milan and Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy
- The 2028 Summer Olympics will be held in Los Angeles, California, United States
- The 2032 Summer Olympics will be held in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia
Association football (Men)
- The 2002 FIFA World Cup – host South Korea and Japan – was won by Brazil
- The 2006 FIFA World Cup – host Germany – was won by Italy
- The 2010 FIFA World Cup – host South Africa – was won by Spain
- The 2014 FIFA World Cup – host Brazil – was won by Germany
- The 2018 FIFA World Cup – host Russia – was won by France
- The 2022 FIFA World Cup – host Qatar – was won by Argentina
Association football (Women)
- The 2003 FIFA Women's World Cup – host United States – was won by Germany
- The 2007 FIFA Women's World Cup – host China – was won by Germany
- The 2011 FIFA Women's World Cup – host Germany – was won by Japan
- The 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup – host Canada – was won by United States
- The 2019 FIFA Women's World Cup – host France – was won by United States
- The 2023 FIFA Women's World Cup – host Australia and New Zealand – was won by Spain
Cricket
- The 2003 Cricket World Cup – host South Africa, Zimbabwe and Kenya – was won by Australia
- The 2007 Cricket World Cup – host West Indies – was won by Australia
- The 2011 Cricket World Cup – host India, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh – was won by India
- The 2015 Cricket World Cup – host Australia and New Zealand – was won by Australia
- The 2019 Cricket World Cup – host England and Wales – was won by England
- The 2023 Cricket World Cup – host India – was won by Australia
Gridiron football

- In the National Football League, the New England Patriots were the dominant franchise of the first two decades of the 21st century, winning six Super Bowls between their first, in 2001, and their most recent, in 2018 and appearing in an additional three others. Head Coach Bill Belichick and quarterback Tom Brady led the team during the stretch, with Brady also leading the Tampa Bay Buccaneers to an additional Super Bowl following the 2020 season. Other teams with multiple Super Bowl appearances over that time period include the Philadelphia Eagles, New York Giants, Kansas City Chiefs, Seattle Seahawks, and Carolina Panthers. Besides Brady, who also won three Associated Press NFL Most Valuable Player Award (MVP), other highly recognized players include quarterback Peyton Manning, who won five MVP awards, the most in history, and quarterback Aaron Rodgers who won three MVPs, who in 2011 set the NFL record for season passer rating. Successful offensive players at other positions include wide receiver Randy Moss, who set the record for most receiving touchdowns in a season with 23 in 2007, wide receiver Michael Thomas, who set the NFL record for most receptions in a season with 149 in 2019, tight end Rob Gronkowski, who became the first tight end to lead the league in receiving touchdowns in 2011, and running back Adrian Peterson, who set the all-time NFL record for rushing yards in a game with 296 in 2007, his rookie year. Key defensive players of the century include safety Ed Reed, who led the league in interceptions three times, linebacker Ray Lewis, who set the career tackles record when he retired in 2012, and linebacker J. J. Watt, who is the only player to record more than 20 quarterback sacks in two different seasons.
- In American college football, the sport saw the creation of the College Football Playoff, the first playoff for NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, the highest level of college football in the U.S. The series was dominated by two teams, the Clemson Tigers and Alabama Crimson Tide, at least one of which has played in every Playoff since its inception in 2014 and between them have won all but one of said championships. Prior to 2014, the method of determining the champion was done via the Bowl Championship Series (BCS), a single championship game that attempted to match the top two teams in the country using a series of polls and computer rankings to choose the top two teams. In the BCS era, the top teams were Alabama, which won three BCS Championships, and Florida State, LSU, and Oklahoma, which won two BCS Championships each. Nick Saban, who led both LSU and Alabama to one and seven national championships respectively, was the most dominant coach of his era, while quarterbacks dominated the Heisman Trophy, winning 16 of 20 during the first two decades of the 21st century. Several controversies over the payment of athletes dominated the sport, with Heisman Trophy winner Reggie Bush being forced to return his award over receiving improper benefits while maintaining amateur status, while officials and media continued to debate the possibility of paying athletes at all levels of college athletics.
- In Canadian football, the league opened the 21st century facing an uncertain financial future, suffering from the failures of the experiment of trying to field Canadian football teams in the United States and having to contract a large number of teams at the end of the 20th century. The league fluctuated between eight and nine teams as two different Ottawa-based franchises failed during the first decade of the 21st century. The league found stability during the 2010s, and showed surprising parity between the teams, with all nine teams appearing in at least one Grey Cup during the 2000s and 2010s, and with only the Montreal Alouettes winning back-to-back titles during those two decades, in 2009 and 2010. Quarterback Anthony Calvillo of the Alouettes was the face of the league during his career, winning three Most Outstanding Player Awards and setting several passing records in the process.
Golf

- The 2002 Ryder Cup was won by Europe 15 and a half to the USA's 12 and a half.
- The 2004 Ryder Cup was won by Europe 18 and a half to the USA's 9 and a half.
- The 2006 Ryder Cup was won by Europe again 18 and a half to the USA's 9 and a half.
- The 2008 Ryder Cup was won by the USA 16 and a half to Europe's 11 and a half.
- The 2010 Ryder Cup was won by Europe 14 and a half to the USA's 13 and a half.
- The 2012 Ryder Cup was won by Europe 14 and a half to the USA's 13 and a half.
- The 2014 Ryder Cup was won by Europe 16 and a half to the USA's 11 and a half.
- The 2016 Ryder Cup was won by USA 17 to Europe's 11.
- The 2018 Ryder Cup was won by Europe 17 and a half to the USA's 10 and a half.
- The 2021 Ryder Cup was won by USA 19 to Europe's 9.
- The 2023 Ryder Cup was won by Europe 16 and a half to the USA's 11 and half.
Motorsport

- Dale Earnhardt died after a last-lap crash during the Daytona 500 in February 2001.
- Michael Schumacher broke many records in the first few years of the century, including the record for most races won (91), most World Championships (7), and most pole positions (68) by the time he retired in 2006. In 2010, he announced his comeback to Formula One after three years out of the sport, retiring again in 2012.
- Sebastian Vettel broke numerous records on his way to becoming Formula One's youngest ever world champion, in 2010 at age 23, and then the youngest ever double world champion, in 2011 at age 24.
- Sébastien Loeb became the most successful rally driver ever, winning the World Rally Championship a record 9 consecutive times between 2004 and 2012. He also set new records for the most wins, podium finishes and points scored.
- Casey Stoner won his second MotoGP world title (2007 and 2011), and announced his retirement from the sport at just 27 years of age, citing disagreement with the direction of the sport and a desire to spend more time with his family. His retirement became effective at the end of the 2012 MotoGP season. Stoner has won every MotoGP-branded race at least once.
- Craig Lowndes became the first driver to reach 100 race wins in the V8 Supercars Championship.
- Lewis Hamilton broke the record for most career pole positions in Formula One in 2019, and the record for most career wins in 2020.
Rugby Union
- 2003 Rugby World Cup – host Australia – was won by England
- 2007 Rugby World Cup – host France – was won by South Africa
- 2011 Rugby World Cup – host New Zealand – was won by New Zealand
- 2015 Rugby World Cup – host England – was won by New Zealand
- 2019 Rugby World Cup – host Japan – was won by South Africa
- 2023 Rugby World Cup – host France – was won by South Africa
Tennis (Men)
- Roger Federer won 20 Grand Slam titles (6 Australian Opens, 1 French Open, 8 Wimbledons, and 5 US Opens) to surpass Pete Sampras' record of 14.
- Roger Federer, Rafael Nadal and Novak Djokovic each completed a Career Grand Slam, winning the singles championships in the Australian Open, French Open, Wimbledon and US Open; Nadal also won the Olympic Singles gold medal in the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics to complete a Golden Career Slam.
- At the 2010 Wimbledon Championships, John Isner and Nicolas Mahut completed the longest tennis match ever. Isner won 6–4, 3–6, 6–7(7), 7–6(3), 70–68.
- In 2019, Rafael Nadal became the first male player to win a single Grand Slam tournament (French Open) 12 times.
Tennis (Women)
- Serena Williams won 23 Grand Slam titles (7 Australian Opens, 3 French Opens, 7 Wimbledons, and 6 US Opens) in the 21st century, to add to her 1999 US Open title. Including a 2017 Australian Open win whilst 8 weeks pregnant
- Maria Sharapova became the first female Russian player to reach No.1 on 22 August 2005. She also retired in 2020.
- China's Li Na won the 2011 French Open, becoming the first player, male or female, from that country to win a Grand Slam.
- Belarusian Victoria Azarenka won the 2012 Australian Open, becoming the first player, male or female, from that country to win a Grand Slam, and also hold the No.1 ranking (taking over from Caroline Wozniacki).
Arts and entertainment
Art

The rise of the Internet and Social Media led to art being democratized and revolutionized.[210] Art websites and spaces such as DeviantArt grew rapidly. New art movements, such as minimalism, craftivism, stuckism, and remodernism, as well as new art forms such as street art, environmental art, and pixel art, rose as well. However, concerns grew over the dilution and commercialization of art.[211]
In the late 2010s, NFTs, unique digital assets that represent ownership or proof of authenticity for a specific item, primarily used for digital art, as a new form of investment asset, began dramatically surging. However, many considered them to be an economic bubble or a Ponzi scheme.[212] In 2022, the NFT market collapsed; a May 2022 estimate was that the number of sales was down over 90% compared to 2021.[213] By September 2023, over 95% of all NFTs had zero monetary value.[214]
Music

At the beginning of the century, the compact disc (CD) was the standard form of music media, but alternative forms of music media started to take its place such as music downloading and online streaming. A resurgence in sales of vinyl records in the 2010s was driven by record collectors and audiophiles who prefer the sound of analog vinyl records to digital recordings. In 2020, for the first time since the 1980s, vinyl surpassed CDs as the primary form of physical media for consumers of music, though both were still surpassed by online streaming, which by the 2020s became the predominant way that people consumed music.[215] As of 2024, the most active music streaming services were YouTube (2 billion monthly music users, 100 million premium subscribers), Spotify (615 million monthly users, 239 million premium subscribers), Tencent Music (576 million monthly users, 106.7 million premium subscribers), NetEase Cloud Music (205.9 million monthly users, 44.1 million premium subscribers), Gaana (185 million monthly users), SoundCloud (175 million monthly users), JioSaavn (100 million monthly users), and Apple Music (60 million subscribers).[216]
Television
As with music, the story of the first three decades of the 21st century was the growth of streaming television services in competition with older forms of television, such as Terrestrial television, cable television, and satellite television. The first major company to dominate the streaming service market was Netflix, which began as a DVD-delivery service in the late 1990s, transitioned into an online media streaming platform initially focused on delivering content produced by studios, then began to produce its own content, beginning with the popular and critically acclaimed series House of Cards in 2013. Netflix's success encouraged the creation of numerous other streaming services, such as Hulu, YouTube Premium, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+, which within a year of its launch overtook Netflix as the most downloaded television streaming application.[217]
Issues and concerns

- Climate change. Climate scientists have reached a consensus that the earth is undergoing significant anthropogenic, i.e. human-induced, global warming.[218] Global warming risks considerable losses in biodiversity and ecosystem services, unless considerable sociopolitical changes are introduced, particularly in patterns of mass consumption and transportation.[219]

- Population. The world's population demographics will shift considerably, with the population of Europe and East Asia predicted to decline considerably and the population of Africa, and to a lesser extent South Asia, to grow considerably, unless there are policy changes. The United Nations estimates world population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050.[221] Most growth will take place in the world's poorer countries, which may slow down the reduction of poverty and combined with the effects of global warming, may lead to large migrations.
- Overconsumption and overpopulation. Such growth raises questions of ecological sustainability and creates many economic and political disruptions. In response, many countries have adopted policies which either force or encourage their citizens to have fewer children, and others have limited immigration or both. Debate exists over what the ultimate carrying capacity of the planet may be; whether or not population growth containment policies are necessary; to what degree growth can safely occur thanks to increased economic and ecological efficiency; and how distribution mechanisms should accommodate demographic shifts. Many developed (high-income) countries (most notably Japan) will experience population decline, and the population debate is strongly tied with discussions about the distribution of wealth.
- Poverty. Poverty remains the root cause of many of the world's other ills, including famine, disease, and insufficient education. Poverty contains many self-reinforcing elements (e.g. it can make education unaffordable, which results in continuing poverty) that aid groups hope to rectify. Progress has been made in reducing poverty, especially in China and India, but increasingly in Africa as well. Microcredit lending has started to prove useful as an anti-poverty tool.[citation needed]

- War. Conflicts continue around the world, such as the Syrian Civil War, the Yemeni Civil War and the Russo-Ukrainian War. Violence continues in the Arab–Israeli conflict. Concern remains about nuclear war and nuclear proliferation and the availability of weapons of mass destruction to rogue groups.
- War on drugs. The legal, social, and military battle by governments against drug cartels show little results in ending drug trading and consumption, and an increase in the lives taken. After 2006 in the Mexican Drug War, more than 100,000 human lives have been lost. Some jurisdictions have enacted a degree of legalization or decriminalization of some kinds of drugs and narcotics, notably several U.S. states legalizing marijuana for recreational or medical use.
- Intellectual property. The increasing popularity of digital formats for entertainment media such as movies and music, and the ease of copying and distributing it via the Internet and peer-to-peer networks, has raised concerns in the media industry about copyright infringement (piracy). Much debate is proceeding about the proper bounds between protection of copyright, trademark and patent rights versus fair use and the public domain, where some argue that such laws have shifted greatly towards intellectual property owners and away from the interests of the general public, while others say that such legal change is needed to deal with a perceived threat of new technologies against the rights of authors and artists (or, as others put it, against the outmoded business models of the entertainment industry). Domain name “cybersquatting” and access to patented drugs and generics to combat epidemics in third-world countries are other IP concerns.
- Technology. Communications and control technology continues to augment the intelligence of individual humans, collections of humans, and machines. Some, notably Ray Kurzweil, have predicted that by the middle of the century there will be a technological singularity if artificial intelligence that outsmarts humans is created. Economists have expressed concerns over technological unemployment due to automation, including AI.
- Civil and political rights, including women's rights, LGBT rights, racial equality, minority rights, and the rights of disabled and individuals with neurodevelopmental disabilities (e.g. autism) are still a work in progress. Women are unable to realize or outright denied their rights in many countries, including India, China[223] and Saudi Arabia, and sexual violence against women is still an enormous problem. Sex-selective abortion has reduced the number of women born worldwide since 1990, mostly because of son preference in China, India, Pakistan, Vietnam, South Korea and other countries. In many countries attitudes towards homosexuality have become more tolerant. Same-sex marriage was legalized in several jurisdictions during the first two decades of the century, but outlawed by constitutional amendment in other places. Meanwhile, some countries such as Uganda and Russia moved to toughen their laws against any sort of homosexual behavior or expression. Political battles over pro- or anti-gay legislation provoked much activism in the streets and on the Internet. Hate groups remain a serious problem, and ethnic minorities have a lower status in many countries, including the United States. Neurological conditions such as ADHD and autism are becoming more understood and recognized.
- Globalization. Advances in telecommunications and transportation, the expansion of capitalism and democracy[disputed – discuss] since the late 1980s, and free trade agreements have resulted in unprecedented global economic and cultural integration. Most economists believe free trade leads to economic growth and benefits most people, including small businesses.[224] In recent years, however, there has been a backlash against globalization and a return to protectionist attitudes among some leaders and nations, most notably United States President Donald Trump and the United Kingdom's decision to leave the European Union.
- Disease. Heart disease, cancer, neonatal conditions and other diseases kill millions annually.[225] Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern. Other diseases, such as COVID-19 and flu variations, may be causes for concern.
Astronomical events
- 8 June 2004: Transit of Venus.
- 23 December 2007: grand conjunction, a galactic conjunction which happens every 26,000 years.
- 2009: Triple conjunction Jupiter–Neptune.
- Solar eclipse of July 22, 2009, total of 6 min 38.8 s, saros 136.
- Solar eclipse of January 15, 2010, annular of 11 min 08 s, saros 141. The longest of the century, and also of the entire millennium.
- 5–6 June 2012: Transit of Venus.
- 11 November 2019: Transit of Mercury.
- Solar eclipse of June 21, 2020, annular of 38 s, saros 137
See also
Notes
- ^ See, for instance, the Lost Decades in Japan.
- ^ See Russian occupation of Donetsk Oblast.
- ^ See Russian occupation of Luhansk Oblast.
References
- ^ "Majority of Americans distrust the government". Reuters. 19 April 2010. Archived from the original on 24 December 2015. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ Lake, David A. "Rational Extremism: Understanding Terrorism in the Twenty-first Century according to Kathii Erick Gitonga" (PDF). quote.ucsd.edu. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 August 2017. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ "Working with Private Industry | Research Pages | The Stimson Center | Pragmatic Steps for Global Security". www.stimson.org. Archived from the original on 3 February 2016. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ Fisher, Marc (20 December 2011). "Arab Spring yields different outcomes in Bahrain, Egypt and Libya". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on 26 October 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ a b Taylor, Adam (29 June 2023). "A historic rise in global conflict deaths suggests a violent new era". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 13 September 2024.
- ^ a b Keating, Joshua (25 January 2024). "It's not your imagination. There has been more war lately. Why the "long peace" may be ending". Vox. Archived from the original on 13 September 2024.
- ^ "Democracy Index 2022". Economist Intelligence Unit.
- ^ Klein, Alice. "Eight low-lying Pacific islands swallowed whole by rising seas". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 25 December 2020. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- ^ "Township in Solomon Islands Is 1st in Pacific to Relocate Due to Climate Change". Scientific American. 15 August 2014. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- ^ "Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment". Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. Archived from the original on 11 May 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ a b "WHO COVID-19 Dashboard". WHO. 21 January 2024. Archived from the original on 6 February 2024. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ a b "The Pandemic's True Death Toll". The Economist. 25 October 2022. Archived from the original on 8 February 2024. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Gopinath, Gita (14 April 2020). "The Great Lockdown: Worst Economic Downturn Since the Great Depression". International Monetary Fund.
- ^ a b "Global offline population steadily declines to 2.6 billion people in 2023". International Telecommunication Union.
- ^ Gent, Edd (8 March 2020). "$100 Genome Sequencing Will Yield a Treasure Trove of Genetic Data". Singularity Hub. Archived from the original on 18 November 2020. Retrieved 25 August 2020.
- ^ Molteni, Megan (19 November 2018). "Now You Can Sequence Your Whole Genome for Just $200". Wired. Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 28 May 2019 – via www.wired.com.
- ^ Frank, Michael (22 September 2023). "US Leadership in Artificial Intelligence Can Shape the 21st Century Global Order". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 8 December 2023. Retrieved 8 December 2023.
Instead, the United States has developed a new area of dominance that the rest of the world views with a mixture of awe, envy, and resentment: artificial intelligence... From AI models and research to cloud computing and venture capital, U.S. companies, universities, and research labs – and their affiliates in allied countries – appear to have an enormous lead in both developing cutting-edge AI and commercializing it. The value of U.S. venture capital investments in AI start-ups exceeds that of the rest of the world combined.
- ^ "What is generative AI?". McKinsey & Company. 19 January 2023. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ Signé, Landry Signe; Dooley, Hanna (28 March 2023). "How space exploration is fueling the Fourth Industrial Revolution". Brookings. Archived from the original on 25 May 2024. Retrieved 8 December 2023.
- ^ "Chandrayaan-3 Details". www.isro.gov.in. Archived from the original on 23 August 2023. Retrieved 14 February 2024.
- ^ "Login". Archived from the original on 10 February 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2007.
- ^ Bansal, Samarth (30 November 2016). "Sex ratio at birth on the decline". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019 – via www.thehindu.com.
- ^ Raposo, V. L. (2019). "The First Chinese Edited Babies: A Leap of Faith in Science". Jbra Assisted Reproduction. 23 (3): 197–199. doi:10.5935/1518-0557.20190042. PMC 6724388. PMID 31436399.
- ^ "Is anxiety increasing in the United States?". Medical News Today. 5 September 2018. Archived from the original on 3 February 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ "Depression". who.int. Archived from the original on 26 December 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ Stack, Steven (28 June 2018). "Why is suicide on the rise in the US – but falling in most of Europe?". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2019.
- ^ "Why the global suicide rate is falling". The Economist. 30 November 2018. Archived from the original on 19 December 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ Carlson, Benjamin (3 July 2010). "Quote of the Day: Google CEO Compares Data Across Millennia". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2019.
- ^ "Eric Schmidt: Every 2 Days We Create As Much Information As We Did Up To 2003". 4 August 2010. Archived from the original on 10 February 2022. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 10 February 2022. Retrieved 10 February 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Harrison Dupré, Maggie (19 January 2024). "Huge Proportion of Internet Is AI-Generated Slime, Researchers Find". Futurism.com.
- ^ "Mobile phone ownership". ITU.
- ^ "Access to electricity (% of population)". World Bank.
- ^ Pruitt, Sarah (3 January 2019). "China Makes Historic Landing on 'Dark Side' of the Moon". HISTORY. Archived from the original on 24 November 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ Chow, Denise (23 August 2023). "India makes historic uncrewed landing on the moon's south pole". NBC News.
- ^ "U.S.-China Relations". Council on Foreign Relations.
- ^ "Poverty headcount ratio at $2.15 a day (2017 PPP) (% of population)". World Bank.
- ^ "By 2030, world will have 8.6bn people, 1.5bn of them in India". The Economic Times. 23 June 2017. Archived from the original on 3 December 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ "World Population Prospects" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- ^ "GHE: Life expectancy and healthy life expectancy". www.who.int. 9 May 2023. Archived from the original on 22 March 2023. Retrieved 9 May 2023.
- ^ "10 million Brits alive today will live to see their 100th birthday". uk.news.yahoo.com. 12 March 2018. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ "Climate change: An 'existential threat' to humanity, UN chief warns global summit". UN News. 15 May 2018. Archived from the original on 23 December 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019.
- ^ Ceballos, Gerardo; Ehrlich, Paul R. (8 June 2018). "The misunderstood sixth mass extinction". Science. 360 (6393): 1080–1081. Bibcode:2018Sci...360.1080C. doi:10.1126/science.aau0191. ISSN 0036-8075. OCLC 7673137938. PMID 29880679. S2CID 46984172.
- ^ Reporter, B. S. (30 April 2014). "India larger than Japan in PPP terms, says WB". Business Standard India. Archived from the original on 25 October 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019 – via Business Standard.
- ^ "US Real Manufacturing Output vs. Employment, 1947 to 2014". Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- ^ "Google Image Result". Google News. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ "Figure 7". Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- ^ Stephane Kasriel (31 October 2018). "The future of work won't be about degrees, it will be about skills". CNBC (Opinion). Archived from the original on 13 December 2020. Retrieved 7 November 2018.
- ^ Johnston, Chris (26 May 2017). "Call to raise retirement age to at least 70". BBC News. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ Emily Jane Fox. "Retirement age must rise – OECD". Archived from the original on 24 October 2020. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ "Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition" Archived 6 April 2006 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 28 June 2007, ISBN 1-55671-159-X
- ^ a b Austin, Peter K; Sallabank, Julia (2011). "Introduction". In Austin, Peter K; Sallabank, Julia (eds.). Cambridge Handbook of Endangered Languages. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88215-6.
- ^ "Mortality in the Democratic Republic of Congo: An ongoing crisis". International Rescue Committee (IRC). 1 May 2007. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ Bora, Kukil (8 December 2014). "Russia To Conduct Observation Flight Over US Under Open Skies Treaty". International Business Times. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "Celebrations as euro hits the streets". BBC News. 1 January 2002. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "The euro becomes the sole legal tender in all euro area countries". European Central Bank. 28 February 2002. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ Carroll, Matt; Pfeiffer, Sacha; Rezendes, Michael; Robinson, Walter V. (6 January 2002). "Church allowed abuse by priest for years". The Boston Globe. Retrieved 12 March 2023.
- ^ "Case study – volcanic eruption in a developing country: Mt Nyiragongo – Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions – Edexcel – GCSE Geography Revision – Edexcel". BBC Bitesize. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ Momodu, Samuel (16 January 2017). "The Sierra Leone Civil War (1991–2002) | The Black Past: Remembered and Reclaimed". Black Past. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "Queen helps CBC TV mark 50th anniversary". CBC. 11 October 2002. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- ^ "Salt Lake City 2002 Winter Olympics – results & video highlights". International Olympic Committee. 13 October 2016. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
- ^ "The Trial of Slobodan Milosevic". The New York Times. 11 February 2002. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "Bahrain now a monarchy". Deseret News. 15 February 2002. Retrieved 12 December 2022.
- ^ Long, Tony (19 January 2002). "Odyssey Turns Its Cameras on Mars". Wired. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "Horror on Egypt fire train". CNN. 20 February 2002. Retrieved 12 December 2022.
- ^ "Savimbi 'died with gun in hand'". BBC News. 25 February 2002. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- ^ Dugger, Celia W. (22 February 2002). "Sri Lanka and Rebels Sign Cease-Fire Agreement". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ^ Sirilal, Ranga (2 January 2008). "Sri Lanka ends ceasefire with Tamil Tigers". Reuters. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ^ "Godhra train burning case accused held after 19 years". The Hindu. 16 February 2021. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ^ Ghosh, Sohini (1 July 2022). "Gulberg Society case: 69 dead, 30 missing, all those convicted out on bail". The Indian Express. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ^ "Estimated casualties in Iraq". Archived from the original on 7 October 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ Razner, Sarah. "15 years after she survived rabies, Jeanna Giese seeks to save others from it". The Reporter. Archived from the original on 19 April 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Lite, Jordan. "Medical Mystery: Only One Person Has Survived Rabies without Vaccine—But How?". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 10 December 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Hamilton, Calvin J. "Dwarf Planet Eris". Solar Views. Archived from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 3 July 2016.
- ^ "Comet probe Deep Impact launches". BBC. 12 January 2005. Archived from the original on 13 December 2006. Retrieved 14 October 2009.
- ^ Malik, Tariq; de Selding, Peter (14 January 2005). "Touchdown on Titan: Huygens Probe Hits its Mark". Space.com. Archived from the original on 10 October 2009. Retrieved 14 October 2009.
- ^ "A New Kind of Solar Storm". NASA Science. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- ^ O'Neil, John; Onishi, Norimitsu (15 October 2006). "US confirms nuclear claim". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 21 November 2020. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ^ Chapin, Kinne (31 January 2013). "The Mooninite Invasion of Boston, 6 Years Later". WGBH-TV. Archived from the original on 31 July 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ^ Cyprus and Malta set to join eurozone in 2008 Archived January 30, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, EurActiv
- ^ Akrotiri and Dhekelia adopt the euro, EUbusiness (ISO 4217 code: VEF). Archived July 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Mercury Flyby 1". Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2008.
- ^ Landler, Mark; Timmons, Heather (21 January 2008). "Stocks Plunge Worldwide on Fears of a U.S. Recession". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 21 November 2008.
- ^ "Hackers Declare War on Scientology – Science News | Science & Technology". Fox News. 10 May 2011. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ "From The Magazine : Radar Online : Scientology is under attack from a faceless cabal of online activists. Has America's most controversial religion finally met its match?". 23 March 2008. Archived from the original on 23 March 2008. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ MAR. "Online group declares war on Scientology". National Post. ISSN 1486-8008. Archived from the original on 28 January 2008. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ "War Breaks Out Between Hackers and Scientology – There Can Be Only One". Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Archived from the original on 14 October 2021. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ "Cayman Islands Bank Gets Wikileaks Taken Offline in U.S. – Updated with Links". Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Archived from the original on 14 October 2021. Retrieved 9 March 2021.
- ^ Gollner, Philipp (29 February 2008). "Judge reverses ruling in Julius Baer leak case". Reuters. Archived from the original on 14 October 2021. Retrieved 9 March 2021.
- ^ "Albania, Croatia become NATO members". msnbc.com. 1 April 2009. Archived from the original on 9 January 2015. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^ "U.N. Security Council to meet on N. Korea launch". CNN. 5 April 2009. Archived from the original on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 5 April 2009.
- ^ "U.N. Launches Library Of World's Knowledge". The Washington Post. 21 April 2009. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- ^ "Jackson dies, almost takes Internet with him". CNN. 26 June 2009. Archived from the original on 25 December 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ^ "NASA Spacecraft Becomes First to Orbit a Dwarf Planet". NASA. 6 March 2015. Archived from the original on 17 April 2016. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Nasa's Dawn probe achieves orbit around Ceres". BBC. 6 March 2015.
- ^ "Nepal earthquake: Hundreds die, many feared trapped". BBC News. 25 April 2015. Archived from the original on 29 June 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ^ Rai, Bhrikuti (26 April 2015). "Nepal earthquake death toll tops 3,200". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 27 March 2022. Retrieved 26 April 2015.
- ^ "Nepal earthquake: 52 dead, hundreds injured in India, huge damage in bordering areas". Hindustan Times. 25 April 2015. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ "Nepal quake: Hundreds dead, history crumbles, Everest shaken". KSL. Associated Press. 25 April 2015. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ Stanglin, Doug. "Hundreds dead as 7.8 magnitude quake rocks Nepal". USA Today. Archived from the original on 25 April 2015. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ "Rubella (German measles) eradicated from Americas". BBC. 29 April 2015. Archived from the original on 23 June 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ^ AFP news agency [@AFP] (3 January 2016). "#BREAKING Saudi Arabia severs ties with Iran, foreign minister says" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "'El Chapo': Sean Penn interviewed Guzman before recapture". BBC News. 10 January 2016. Archived from the original on 10 January 2016. Retrieved 10 January 2016.
- ^ "Iran nuclear deal: 'New chapter' for Tehran as sanctions end". BBC. 17 January 2016. Archived from the original on 17 January 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- ^ "Shih Ming-te fails to meet threshold, ends candidacy". taipeitimes.com. 16 September 2015. Archived from the original on 15 January 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2019.
- ^ Botelho, Greg (28 January 2016). "Zika virus spreading explosively". CNN. Archived from the original on 28 January 2016. Retrieved 28 January 2016.
- ^ "UN: World facing greatest humanitarian crisis since 1945". BBC News. 11 March 2017. Archived from the original on 11 March 2017. Retrieved 11 March 2017.
- ^ "Brexit: Article 50 has been triggered - what now?". BBC News. 29 March 2017. Archived from the original on 3 January 2020. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- ^ "SpaceX Launches a Satellite With a Partly Used Rocket". The New York Times. 30 March 2017. Archived from the original on 6 September 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- ^ "Success for SpaceX 're-usable rocket'". BBC News. 31 March 2017. Archived from the original on 5 May 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- ^ "Rioters storm Paraguay congress and set it on fire after vote to extend president's term". France 24. 1 April 2017. Archived from the original on 7 May 2022. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- ^ "Catalonia declares independence from Spain as political crisis deepens". CNN. 27 October 2017. Archived from the original on 6 November 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ^ "Catalans declare independence as Madrid imposes direct rule". BBC. 27 October 2017. Archived from the original on 4 December 2020. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ^ "Elon Musk's Falcon Heavy rocket launches successfully". BBC News. 6 February 2018. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- ^ "Pyeongchang 2018 Olympics – Next Winter Olympic Games in Korea". Olympic.org. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ Carrington, Damian (19 March 2019). "School climate strikes: 1.4 million people took part, say campaigners". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ "Sudan military says it has seized power". BBC News. 11 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ "Hundreds killed, 450 injured as explosions rock Catholic churches during Easter mass". The Sydney Morning Herald. 22 April 2019. Retrieved 22 April 2019.
- ^ "Deepest Submarine Dive in History, Five Deeps Expedition Conquers Challenger Deep" (PDF). Five Deeps. 13 May 2019. Retrieved 13 May 2019.
- ^ Laville, Sandra; Watts, Jonathan (20 September 2019). "Across the globe, millions join biggest climate protest ever". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ McMullen, Jane (25 January 2021). "Covid-19: Five days that shaped the outbreak". BBC News. BBC. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ "Did Floyd Protests Lead to a Virus Surge? Here's What We Know". The New York Times. 1 July 2020. Archived from the original on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- ^ Detrow, Scott; Khalid, Asma (7 November 2020). "Biden Wins Presidency, According To AP, Edging Trump In Turbulent Race". NPR. Archived from the original on 25 December 2020. Retrieved 7 November 2020.
- ^ "Military moves in to help mass evacuation from Australian bushfires". CBC News. Archived from the original on 23 December 2020. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ Marnie, O'Neill (1 January 2020). "Half a billion animals perish in bushfires". News.com.au. Archived from the original on 3 January 2020. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- ^ "Croatia elects centre-left challenger Zoran Milanovic as president". BBC News. 6 January 2020. Archived from the original on 8 April 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- ^ "Sultan Qaboos of Oman dies aged 79". BBC News. 11 January 2020. Archived from the original on 15 January 2020. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ "Oman's new ruler Haitham bin Tariq takes oath: newspapers". Reuters. 11 January 2020. Archived from the original on 11 January 2020. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ "Taiwan election: Tsai Ing-Wen wins landslide in rebuke to China". The Guardian. 11 January 2020. Archived from the original on 3 February 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "Taiwan opposition candidate admits defeat in presidential election". Reuters. 11 January 2020. Archived from the original on 22 January 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "Election Result By Parties Votes For The 10th Regional Legislators Elections (National Level Public Officials Election-Taiwan, 2020" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 November 2022. Retrieved 6 January 2023.
- ^ "After months of COVID delays, African free trade bloc launches". Al Jazeera. 1 January 2021. Retrieved 3 January 2021.
- ^ "Guterres hails entry into force of treaty banning nuclear weapons". UN News. 22 January 2021. Archived from the original on 24 April 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ^ "COVID-19: 100 million coronavirus cases recorded worldwide – a year after virus first officially diagnosed". Sky News. 26 January 2021. Archived from the original on 14 February 2021. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- ^ "Military takes control of Myanmar; Suu Kyi reported detained". ABC. 1 February 2021. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ mars.nasa.gov. "Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover". mars.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Agle, D.C.; Fox, Karen; Johnson, Alana; Schmid, Deb (3 June 2021). "NASA's Juno to Get a Close Look at Jupiter's Moon Ganymede". NASA. Archived from the original on 3 June 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
On Monday, June 7 [...] NASA's Juno spacecraft will come within 645 miles (1,038 kilometers) of the surface of Jupiter's largest moon, Ganymede. The flyby will be the closest a spacecraft has come to the solar system's largest natural satellite since NASA's Galileo spacecraft made its penultimate close approach back on May 20, 2000.
- ^ Berger, Eric (12 January 2021). "NASA extends Juno, turning spacecraft into an Io, Europa, and Ganymede explorer". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on 3 June 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
As part of a research plan submitted by Scott Bolton, Juno's principal investigator, the spacecraft will fly to within 1,000km of the surface of Ganymede...
- ^ "Afghanistan conflict: Kabul falls to Taliban as president flees". BBC News. 16 August 2021. Archived from the original on 16 August 2021. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ "2022 Olympics – Next Winter Olympic Games | Beijing 2022". International Olympic Committee. 28 May 2020. Archived from the original on 27 February 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ "Cop15: historic deal struck to halt biodiversity loss by 2030". The Guardian. 19 December 2022. Retrieved 19 December 2022.
- ^ "COP15: Nations reach 'historic' deal to protect nature". BBC News. 19 December 2022. Retrieved 19 December 2022.
- ^ "Brazilian football legend Pele dies at age 82". www.aljazeera.com. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Croatia set to join the euro area on 1 January 2023: Council adopts final required legal acts". European Council/Council of the European Union. 12 July 2022. Archived from the original on 25 July 2022. Retrieved 16 July 2022.
- ^ Buckley, Julia (2 January 2023). "This popular European country just got a new currency". CNN. Archived from the original on 3 January 2023. Retrieved 3 January 2023.
- ^ "Earthquake Kills More Than 110 People in Turkey, Syria". Bloomberg.com. 6 February 2023. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- ^ "Powerful quake kills at least 360 people in Turkey, Syria". AP NEWS. 6 February 2023. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- ^ Petersen, Shelleygan (4 February 2024). "President Hage Geingob is dead". The Namibian. Archived from the original on 4 February 2024. Retrieved 4 February 2024.
- ^ "Hage Geingob, Namibia's president, dies aged 82 after cancer treatment". The Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 4 February 2024. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 4 February 2024.
- ^ "El Salvador's Bukele is already claiming a big election win, but a troubled count delays results". AP News. 5 February 2024. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "After Nayib Bukele's crushing, unconstitutional victory, what next?". The Economist. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ Jackson, Patrick; Buschschlüter, Vanessa (6 February 2024). "Sebastián Piñera: Former president of Chile dies in helicopter crash". BBC. Archived from the original on 7 February 2024. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "Azerbaijan's president is likely to win election after a blitz offensive reclaimed Karabakh region". Associated Press. 7 February 2024. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "Imran Khan loyalists win shock victory in Pakistan election". www.ft.com. Retrieved 9 February 2024.
- ^ "Sweden officially joins NATO". NATO. 7 March 2024. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ "Sweden finally joins Nato after nearly two-year wait". The Guardian. 7 March 2024. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ "Portugal election sees above-average turnout in very tight contest". POLITICO. 10 March 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ^ Vock, Ido (21 March 2024). "Luís Montenegro: Centre-right leader invited to form minority government". BBC. Archived from the original on 21 March 2024. Retrieved 21 March 2024.
- ^ "Haiti's prime minister Ariel Henry resigns as law and order collapses". 12 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ "World's first major act to regulate AI passed by European lawmakers". CNBC. 14 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ Grolier- the new book of knowledge, section "E"
- ^ "NASA News Conference: Evidence of Liquid Water on Today's Mars". NASA. 28 September 2015. Archived from the original on 18 July 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Greicius, Tony (13 March 2015). "Juno Overview". Archived from the original on 7 September 2018. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
- ^ Moss, Trefor (3 January 2019). "China Lands Probe on the 'Dark Side' of the Moon". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 12 April 2019. Retrieved 3 January 2019.
- ^ Ryan, Jackson (13 February 2019). "NASA's history-making Mars rover Opportunity declared dead". CNET. Archived from the original on 11 April 2019. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- ^ Grossman, Lisa; Conover, Emily (10 April 2019). "The first picture of a black hole opens a new era of astrophysics". Science News. Archived from the original on 27 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ Garner, Rob (11 July 2022). "NASA's Webb Delivers Deepest Infrared Image of Universe Yet". NASA. Archived from the original on 12 July 2022. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ "Chandrayaan-3".
- ^ "Higgs boson-like particle discovery claimed at LHC". BBC News. 4 July 2012. Archived from the original on 16 November 2020. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ "The 21st Century and the 3rd Millennium". aa.usno.navy.mil. Archived from the original on 2 October 2019. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- ^ Lixion A. Avila (4 January 2006). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Storm Alpha" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 22 March 2023.
- ^ Miller, Susan. "Tropical Storm Eta expected to intensify into the season's 12th hurricane on Monday". USA TODAY. Retrieved 23 March 2023.
- ^ "Fujita Tornado Damage Scale". www.spc.noaa.gov.
- ^ "Tornado Scale - The Enhanced Fujita Scale | TornadoFacts.net". www.tornadofacts.net.
- ^ "Enhanced Fujita Scale". Environment Canada. 10 May 2013.
- ^ National Weather Service (15 May 2023). "May 20, 2013: The Day an EF-5 Tornado Struck the OKC Metro" (StoryMap). ArcGIS StoryMaps. Norman, Oklahoma: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 5 May 2024.
- ^ National Weather Service (31 May 2023). "May 31, 2013: Tornado Outbreak & Historic Flooding" (StoryMap). ArcGIS StoryMaps. Norman, Oklahoma: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 5 May 2024.
- ^ Jeff Masters (4 June 2013). "Largest Tornado on Record: the May 31 El Reno, OK EF-5 Tornado". Weather Underground. The Weather Company. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ Bluestein, Howard B.; Snyder, Jeffrey C.; Houser, Jana B. (2015). "A Multiscale Overview of the el Reno, Oklahoma, Tornadic Supercell of 31 May 2013". Weather and Forecasting. 30 (3): 525–552. Bibcode:2015WtFor..30..525B. doi:10.1175/WAF-D-14-00152.1.
- ^ Bernold Feuerstein; Thilo Kühne (September 2015). "A violent tornado in mid-18th century Germany: the Genzmer Report". ECSS 2015 - European Conference on Severe Storms at: Wiener Neustadt, Austria. 8. European Severe Storms Laboratory. doi:10.13140/RG.2.1.3733.8085. Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- ^ Bates, Sabrina (20 March 2024). "STEM Spotlight: Storm Prediction Center meteorologist makes history for women". KOCO. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center meteorologist became first woman to issue Severe Thunderstorm Watch". Fox Weather. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "A conversation with Oklahoma meteorologist Liz Leitman, the first woman to issue a thunderstorm watch". KOSU. 28 February 2023.
- ^ "WICKER, COLLEAGUES INTRODUCE TORNADO ACT". Roger Wicker. 26 April 2023. Retrieved 26 April 2023.
- ^ Pieter Groenemeijer (ESSL); Lothar Bock (DWD); Juan de Dios Soriano (AEMet); Maciej Dutkiewicz (Bydgoszcz University of Science and Technology); Delia Gutiérrez-Rubio (AEMet); Alois M. Holzer (ESSL); Martin Hubrig; Rainer Kaltenberger; Thilo Kühne (ESSL); Mortimer Müller (Universität für Bodenkultur); Bas van der Ploeg; Tomáš Púčik (ESSL); Thomas Schreiner (ESSL); Miroslav Šinger (SHMI); Gabriel Strommer (ESSL); Andi Xhelaj (University of Genova) (30 July 2023). "The International Fujita (IF) Scale" (PDF). European Severe Storms Laboratory. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ First, Jennifer M.; Carnahan, Megan; Yu, Mansoo; Lee, Sangwon; Houston, J. Brian (19 February 2024). "'Recovering from Tornado Brain': A Qualitative Analysis of Long-Term Needs after One of the Deadliest Tornadoes in U.S. History". Clinical Social Work Journal. The University of Tennessee and University of Missouri via Springer Science+Business Media: 1–11. doi:10.1007/s10615-024-00926-1. ISSN 1573-3343. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "Neurosurgeons successfully implant 3D printed skull". Wired. 26 March 2014. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ "The Artificial Pancreas Device System". FDA. 30 August 2018.
- ^ "Researchers 3D-print heart from human patient's cells". CNN. 4 April 2019. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ "Human Genome Project". genome.gov. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ "Measuring digital development: Facts and figures 2023". Telecommunication Development Bureau, International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ "Total Midyear Population for the World: 1950-2050"". International Programs Center for Demographic and Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 17 April 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Bodeen, Christopher (8 August 2010). "Asia flooding plunges millions into misery". The Associated Press. Archived from the original on 4 September 2010. Retrieved 8 August 2010.
- ^ Masood, Salman and Adam B. Ellick. Floods in Pakistan Kill at Least 700 Archived 26 December 2020 at the Wayback Machine. NYTimes.
- ^ "UN voices Pakistan flood fears as death toll soars". BBC. 31 July 2010. Archived from the original on 2 August 2018. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- ^ Khan, Ismail (30 July 2010). "400 Killed in Flooding in Pakistan, Officials Say". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 31 December 2019. Retrieved 30 July 2010.
- ^ "Thousands trapped by Pakistan floods; 900 dead". Archived from the original on 12 August 2010. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ "Deaths From Pakistan Floods May Reach 3,000, Rescue Service Official Says". Bloomberg. 31 July 2010. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ CNN Archived 21 October 2020 at the Wayback Machine Report: Superstorm Sandy. Retrieved 30 October 2012.
- ^ Cleveland News Archived 20 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine Superstorm Sandy. Retrieved 30 October 2012.
- ^ Telegraph.co.uk Archived 28 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine News Report. 30 October 2012.
- ^ "'Our children die in our hands': Floods ravage South Sudan". Associated Press. 1 January 2021. Archived from the original on 1 January 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- ^ "Floods-hit Sudan facing 'unprecedented challenges', UN warns". aljazeera.com. Al Jazeera English. 25 September 2020. Archived from the original on 8 December 2020. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- ^ "BP Will Pay For Gulf Oil Spill Disaster, CEO Says". NPR. 3 May 2010. Archived from the original on 4 May 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2010.
- ^ "Choppy Seas Hinder Effort To Contain Oil Spill" Archived 13 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine, National Public Radio, 30 April 2010
- ^ "Oil spill full of methane, adding new concerns". msnbc. 18 June 2010. Archived from the original on 23 September 2020. Retrieved 20 June 2010.
- ^ "Document Shows BP Estimates Spill up to 100,000 Bpd". ABC News. 20 June 2010. Archived from the original on 24 June 2010. Retrieved 20 June 2010.
- ^ "Seafloor Exit" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 July 2010. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
- ^ Murphy, Steven (30 August 2018). "Art Explained: How the Internet changed the art world". CNN.
- ^ Bandoim, Lana (24 November 2017). "How the internet is transforming the art world". The Week.
- ^ Hawkins, John (13 January 2022). "NFTs, an overblown speculative bubble inflated by pop culture and crypto mania". The Conversation.
- ^ Vigna, Paul (3 May 2022). "NFT Sales Are Flatlining". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Yang, Maya (22 September 2023). "The vast majority of NFTs are now worthless, new report shows". The Guardian.
- ^ Dean, Grace (14 September 2020). "Americans are spending more on vinyl records than CDs for the first time since the 1980s". Business Insider. Insider Inc. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ "How many users do Spotify, Apple Music and other big music streaming services have?". Music Ally. 19 February 2020. Archived from the original on 12 January 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ Kissel, Chris (22 January 2021). "The 10 Most Popular Streaming TV Services of 2020". Money Talks News. Archived from the original on 25 January 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ Oreskes, Naomi (2004). "The Scientific Consensus on Climate Change". Science. 306 (5702): 1686. doi:10.1126/science.1103618. PMID 15576594.
- ^ "What the World Would Look Like if All the Ice Melted". 1 September 2013. Archived from the original on 11 January 2017. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
- ^ World population projected to reach 7 billion in 2011 ". PRB. October 25, 2011.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022" (PDF). UN. Retrieved 6 August 2023.
- ^ "Global Nuclear Arsenal Declines, But Future Cuts Uncertain Amid U.S.-Russia Tensions". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 17 June 2019. Archived from the original on 2 July 2019. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ^ Fry, Lisa. "Chinese Women and Economic Human Rights" (PDF). Josef Korbel School of International Studies University of Denver. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2012. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ Partington, Richard (13 August 2018). "Is free trade always the answer?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 9 November 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2019 – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ "The top 10 causes of death". www.who.int.
Further reading
- Allitt, Patrick N. (2020). "America after the Cold War: The First 30 Years". The Great Courses.
- Andersson, Jenny (2018). The future of the world: Futurology, futurists, and the struggle for the post cold war imagination. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-254550-3.
- Ahram, Ariel I. (2020). War and conflict in the Middle East and North Africa. Polity. ISBN 978-1-5095-3281-0.
- Aziz, Nusrate; Asadullah, M. Niaz (2017). "Military spending, armed conflict and economic growth in developing countries in the post–Cold War era" (PDF). Journal of Economic Studies. 44 (1): 47–68. doi:10.1108/JES-01-2015-0021.
- Brands, Hal (2016). Making the unipolar moment: U.S. foreign policy and the rise of the post-Cold War order. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-1-5017-0272-3.
- Brügger, Niels, ed. (2017). Web 25: histories from the first 25 years of the World Wide Web. Digital formations. New York: Peter Lang. ISBN 978-1-4331-3269-8.
- Cameron, Fraser (2005). US foreign policy after the Cold War: global hegemon or reluctant sheriff? (2nd ed.). Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-35864-4. OCLC 57694857.
- Cassani, Andrea; Tomini, Luca (2018). Autocratization in post-Cold War political regimes. New York, NY: Springer. ISBN 978-3-030-03124-4.
- Clapton, William, ed. (2014). Risk and Hierarchy in International Society: Liberal Interventionism in the Post-Cold War Era. Palgrave Macmillan UK. ISBN 978-1-137-39636-5.
- Dai, Jinhua; Rofel, Lisa, eds. (2018). After the Post–Cold War: The Future of Chinese History. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-1-4780-0038-9.
- Duong, Thanh (2017) [2002]. Hegemonic globalisation: U.S. centrality and global strategy in the emerging world order. Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-3013-5.
- Gertler, Mark; Gilchrist, Simon (2018). "What happened: Financial factors in the great recession". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 32 (3): 3–30. doi:10.1257/jep.32.3.3.
- Harrison, Ewan (2004). The Post-Cold War International System: Strategies, Institutions and Reflexivity. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-32836-4.
- Henriksen, Thomas H. Cycles in US Foreign Policy Since the Cold War (Palgrave Macmillan, 2017) excerpt.
- Howe, Joshua P. Behind the curve: science and the politics of global warming (U of Washington Press, 2014).
- Jackson, Robert J. and Philip Towle. Temptations of Power: The United States in Global Politics after 9/11 (2007)
- Lamy, Steven L., et al. Introduction to global politics (4th ed. Oxford UP, 2017)
- Mandelbaum, Michael The Rise and Fall of Peace on Earth (Oxford UP, 2019) why so much peace 1989–2015. excerpt
- Maull, Hanns W., ed. The rise and decline of the post-Cold War international order (Oxford UP, 2018).
- Pekkanen, Saadia M., John Ravenhill, and Rosemary Foot, eds. Oxford handbook of the international relations of Asia (Oxford UP, 2014), comprehensive coverage.
- Pocket world in figures 2021. London: Economist Publications. 2020. ISBN 9781788164979.
- Ravenhill, John, ed. Global political economy (5th ed. Oxford UP, 2017) excerpt
- Reid-Henry, Simon. Empire of Democracy: The Remaking of the West Since the Cold War (2019) excerpt
- Rosenberg, Jerry M. (2012). The Concise Encyclopedia of The Great Recession 2007–2012 (2nd ed.). Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-8340-6.
- Rubin, Robert, and Jacob Weisberg. In an uncertain world: tough choices from Wall Street to Washington (2015).
- Rudolph, Peter (February 2020). The Sino-American World Conflict (Report). SWP Research Paper. Vol. 3. German Institute for International and Security Affairs. doi:10.18449/2020RP03.
- Schenk, Catherine R. International economic relations since 1945 (2nd ed. 2021).
- Smith, Rhona K.M. et al. International Human Rights (4th ed. 2018)
- Smith, Rhona KM. Texts and materials on international human rights (4th ed. Routledge, 2020).
- Strong, Jason. The 2010s: Looking Back At A Dramatic Decade (2019) online
- Taylor-Gooby, Peter, Benjamin Leruth, and Heejung Chung, eds. After austerity: Welfare state transformation in Europe after the great recession (Oxford UP, 2017).
- The World in 2020. London: Economist Publications. 2019. OCLC 1129588760.
- Tooze, Adam (2018). Crashed: How a Decade of Financial Crises Changed the World. New York: Viking. ISBN 978-0-670-02493-3.
- Tooze, Adam. Shutdown: How Covid Shook the World's Economy (2021).
- United Nations. World Economic Situation and Prospects 2020 (2020) online annual reports
- United Nations. World Economic and Social Survey 2010 – Retooling Global Development (2010) online
External links
- Reuters – The State of the World The story of the 21st century
- Long Bets Foundation to promote long-term thinking
- Century Seasons Archived 20 June 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- Long Now Long-term cultural institution
- Scientific American Magazine (September 2005 Issue) The Climax of Humanity
- MapReport 21st Century Event World Map
